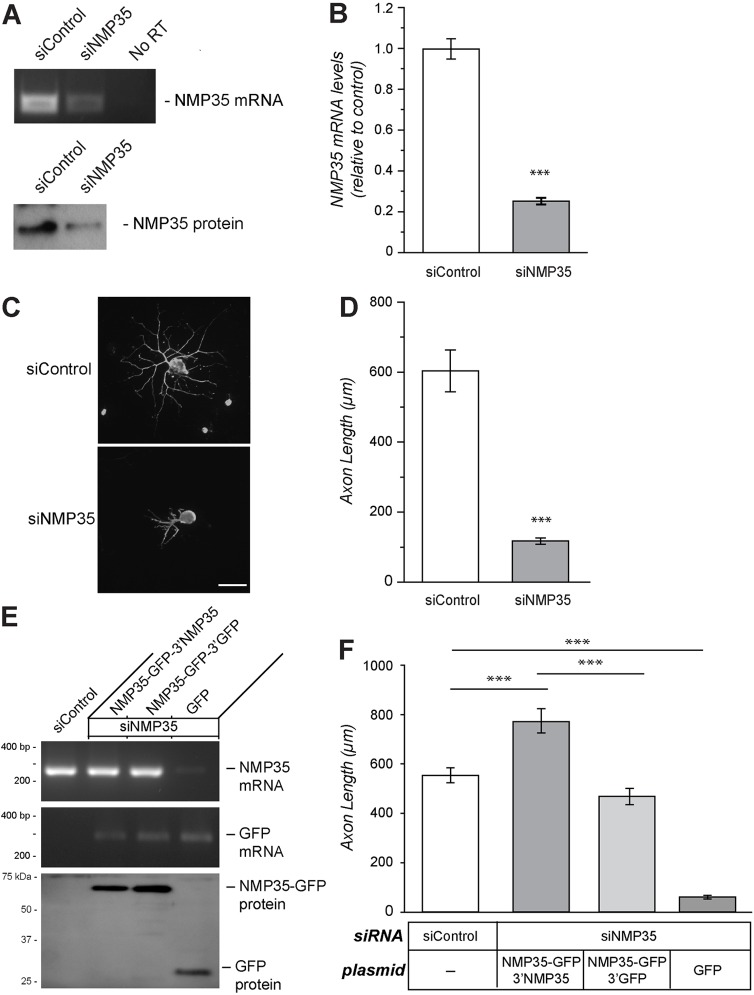
Fig. 5.
Depletion of NMP35 mRNAs in the DRG neurons attenuates axonal outgrowth. (A) DRG cultures transfected with siRNA targeting NMP35 (siNMP35) mRNA or a non-targeting control (siControl) show reduced NMP35 mRNA and protein at 72 hours post-transfection by RT-PCR and immunoblotting, respectively. (B) RTqPCR: siNMP35 reduced endogenous NMP35 mRNA levels by ∼80%. (C,D) Depletion of NMP35 mRNA from DRG cultures decreases axonal growth. Representative neurofilament heavy (NF H)-stained images are shown in C. Quantification of average axon length for neurons transfected with siNMP35 versus siControl after 72 hours in vitro is shown in D. Scale bar: 100 µm. (E,F) To test for potential off-target effects of the siNMP35, neurons were co-transfected with cell-body-restricted (NMP35-GFP-3′GFP) versus axonally targeted (NMP35-GFP-3′NMP35) constructs; transfection with GFP was used as a control. (E) Representative RT-PCR and immunoblotting for NMP35 mRNA and NMP35-GFP mRNA and proteins. Upon co-transfection with siNMP35 and NMP35-GFP constructs, NMP35 mRNA levels were rescued to near-endogenous levels. GFP mRNA levels were relatively equivalent for the two NMP35-GFP and the GFP transfections. Immunoblotting confirmed expression of NMP35-GFP protein. (F) Analysis of axonal growth in these co-transfection experiments showed the expected reduction in axon length comparing siNMP35+GFP and siControl transfections. Both of the NMP35-GFP constructs rescued axonal outgrowth deficit seen with siNMP35, with the axonally targeting NMP35-GFP-3′NMP35 increasing axonal growth above the siControl-transfected cultures. siNMP35+GFP showed significant reduction in axonal outgrowth compared with siControl-, NMP35-GFP-3′NMP35- and NMP35-GFP-3′GFP-transfected neurons (n≥25 from at least three separate transfection experiments; ***P≤0.001 by Student's t-test for B, D and F). Values in B, D and F are means±s.e.m.