Fig. 6.
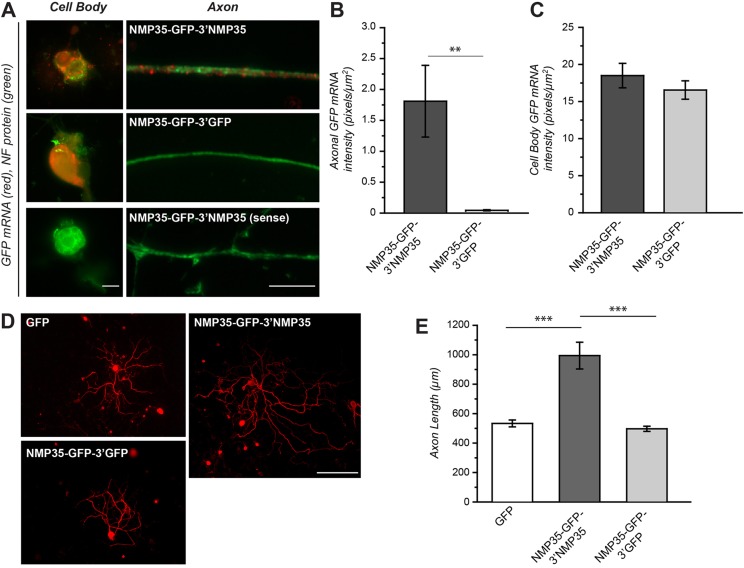
Axonal targeting of NMP35 mRNA is sufficient to increase axonal outgrowth. To determine whether targeting NMP35-GFP fusion protein for axonal synthesis might contribute to growth, we transduced cultured DRG neurons with the LV preparations used in Fig. 4 to overexpress axonally targeted versus cell-body-restricted NMP35 mRNA (NMP35-GFP-3′NMP35 and NMP35-GFP-3′GFP, respectively). (A–C) NMP35-GFP-3′NMP35- and NMP35-GFP-3′GFP-transduced cultures were processed for FISH for GFP mRNA. Representative exposure-matched images of cell bodies and axon shafts are shown in A. Here, GFP mRNA is only seen in axons of NMP35-GFP-3′NMP35-transduced cultures. Quantification of axonal and neuronal cell body GFP mRNA signals for multiple cultures is shown in B and C, respectively. There is no axonal GFP mRNA signal above background in the NMP35-GFP-3′GFP-transduced cultures, whereas cell body signals are not significantly different between the NMP35-GFP-3′GFP- and NMP35-GFP-3′NMP35-transduced cultures (**P≤0.01 by Student's t-test). (D) Representative montage images of neurons expressing GFP, NMP35-GFP-3′NMP35 and NMP35-GFP-3′GFP for 72 hours and then stained for neurofilament heavy (NF H) are shown. (E) Quantification of axon length of neurons transduced with GFP, NMP35-GFP-3′NMP35 or NMP35-GFP-3′GFP is shown (n≥25 neurons in at least three separate transduction experiments; **P≤0.01; ***P≤0.001 by Student's t-test). Scale bars: 10 µm (A); 200 µm (D).