Figure 6.
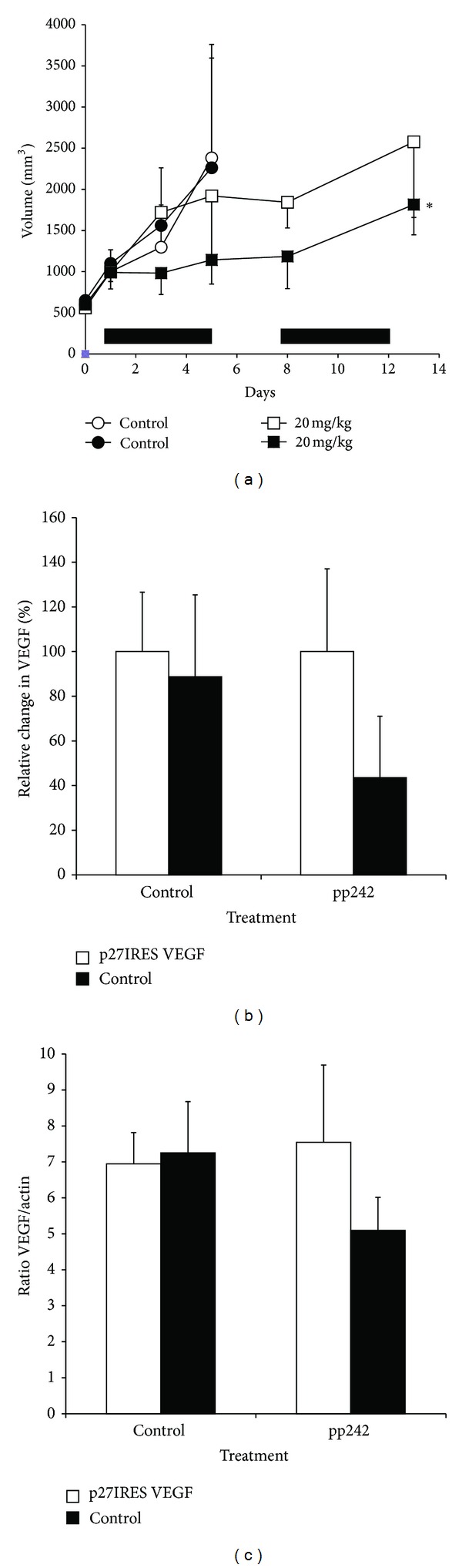
Antitumor effects of the active-site mTOR inhibitor, pp242, are ameliorated by exogenous VEGF expression. (a) NOD/SCID mice (4 mice/group) were challenged subcutaneously with 1 × 106 HS Sultan cells stably transfected with exogenous VEGF expressing p27IRES-VEGF transfected cells (open symbols) on the right flank and 1 × 106control (Rev)p27IRES-VEGF transfected cells (filled symbols) on the left flank. When tumor size reached approximately 500 mm3, mice were randomly assigned to receive vehicle alone or 20 mg/kg temsirolimus IP for 10 days, as described in “Materials and Methods.” Mice in the control group were euthanized by day 7 because the tumors had reached end-point criteria. Results are presented as tumor volume (mean ± SEM). Solid bars on x-axis denote days of IP treatment. Asterisk denotes significant difference (P < 0.05) between the growth curves for p27IRES-VEGF transfected cells (filled squares) and (Rev)p27IRES-VEGF transfected cells (open squares) in the group of mice treated with 20 mg/kg pp242. (b) Relative change in VEGF expression. Isogenic HS Sultan tumors were grown on either flank of NOD/SCID mice (4 mice/group) that were treated with temsirolimus or vehicle control as described in Materials and Methods section. Tumors were harvested, and VEGF levels were measured in the tumor lysates by ELISA. Values are presented as the relative % change of VEGF expression between p27IRES-VEGF (open bars) and (Rev)p27IRES-VEGF (closed bars) tumors isolated from temsirolimus (20 mg/kg) or vehicle control-treated mice. (c) VEGF expression was also measured in the tumor lysates by immunoblot. VEGF and actin levels were quantified by densitometry analysis and are shown as the ratios of VEGF/actin in p27IRES-VEGF transfected (open bars) and (Rev)p27IRES-VEGF transfected tumors in control or temsirolimus (20 mg/kg) treated mice. Values are the means ± SEM.
