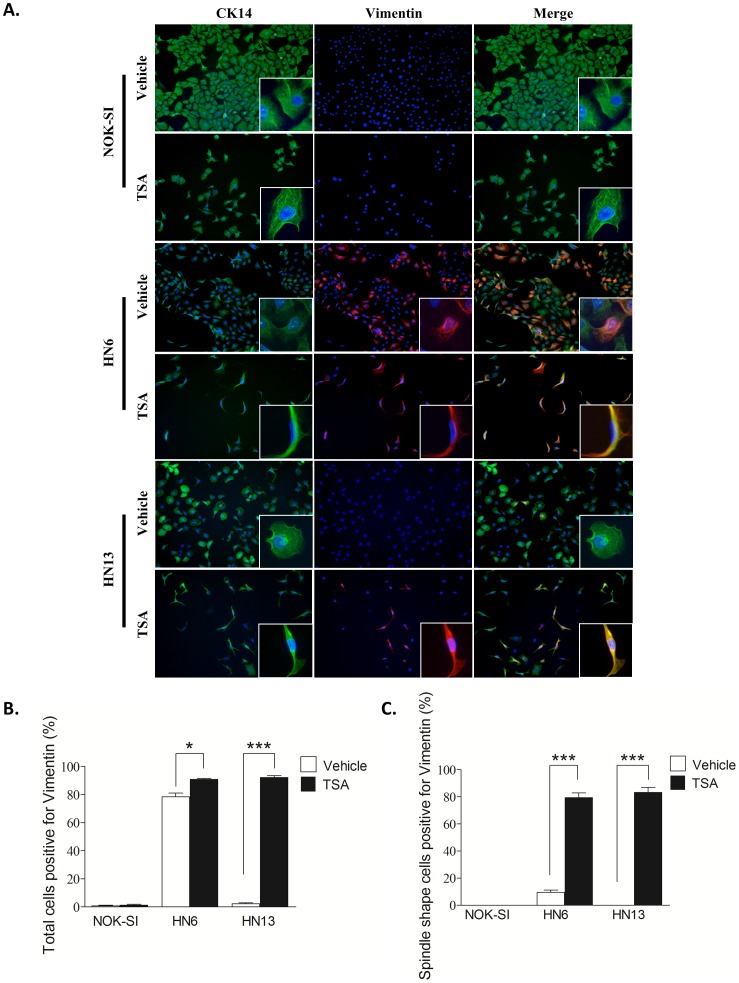
Figure 3. Chemically induced chromatin acetylation leads to activation of the EMT phenotype.
Inhibition of histone deacetylase induces vimentin expression in HNSCC cells and acquisition of the spindle shaped morphology. (A) Representative examples of morphological changes and expression of the cytokeratin 14 (CK14) epithelial cell marker and the vimentin mesenchymal marker. Note that normal keratinocytes express CK14 in the presence of vehicle or TSA and cell morphology is continuously epithelioid (cobblestone or discoid appearance). Both HN6 and HN13 cells express CK14 and an epithelioid shape (A, vehicle). Following TSA treatment, HN6 and HN13 express vimentin and become spindle shaped. (B) Graphics represent the percentage of cells positive for vimentin following TSA or vehicle treatment. TSA-induced chromatin acetylation results in increased vimentin expression in HN6 and HN13 cells (*p<0.05 and ***p<0.001). (C) Graphic representing vimentin expression in spindle shaped cells (tumor cells with EMT-like morphology). HN6 and HN13 cells display significant increases in vimentin expression after TSA treatment (***p<0.001).