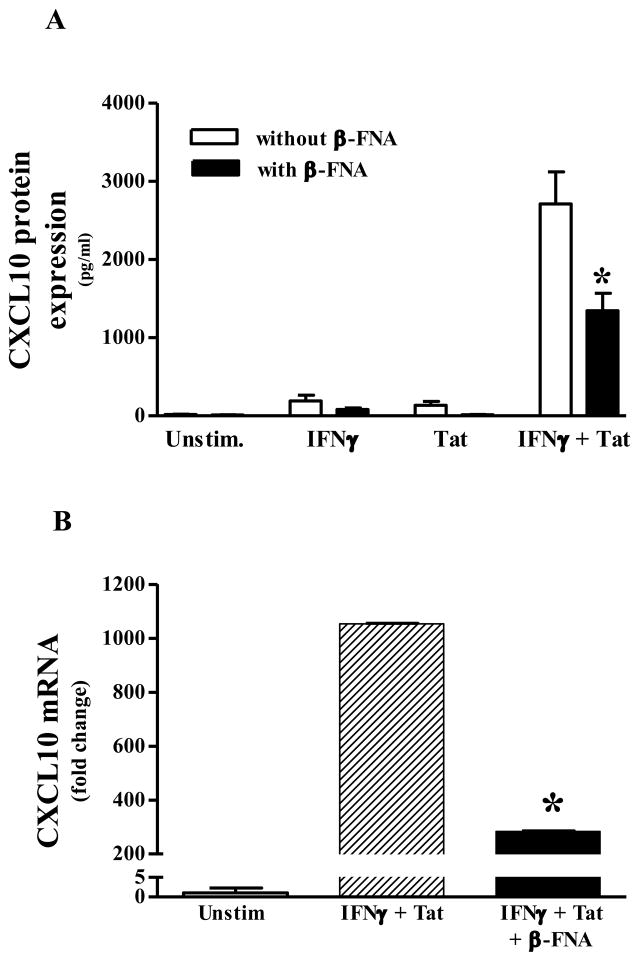
Fig. 1.
β-FNA inhibits proinflammatory-induced CXCL10 expression in normal human astrocytes. Panel A) β-FNA effects on CXCL10 protein expression: In the presence or absence or β-FNA (10 μM), normal human astrocytes were exposed to human recombinant IFNγ (10 ng/ml), HIV-1 Tat1–72 (100 nM), IFNγ + HIV-1 Tat1–72, or serum free medium alone for 24 h. CXCL10 protein levels in the media were then measured by ELISA. The data represent mean + S.E.M of 9 independent experiments. Two-way ANOVA (β-FNA treatment × stimulus) indicated a significant effect of β-FNA (p < 0.009), stimulus (p < 0.0001) and an interaction (p < 0.0005). Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons indicated that β-FNA significantly (* p < 0.001) inhibited IFNγ + HIV-1 Tat1–72-induced CXCL10 expression. Panel B) β-FNA effects on CXCL10 mRNA expression: In the presence or absence or β-FNA (10 μM), normal human astrocytes were exposed to human recombinant IFNγ (10 ng/ml) + HIV-1 Tat1–72 (100 nM) or in serum free medium alone for 8 h. Total RNA was isolated and CXCL10 and GAPDH mRNA assessed by real-time PCR. The data represent mean + S.E.M of 6 independent experiments. Analysis of ΔCT values by one-way ANOVA followed by Newman-Keuls multiple comparisons indicated that β-FNA significantly inhibited IFNγ + HIV-1 Tat1–72-induced CXCL10 mRNA expression. * p < 0.05 vs. IFNγ + HIV-1 Tat1–72