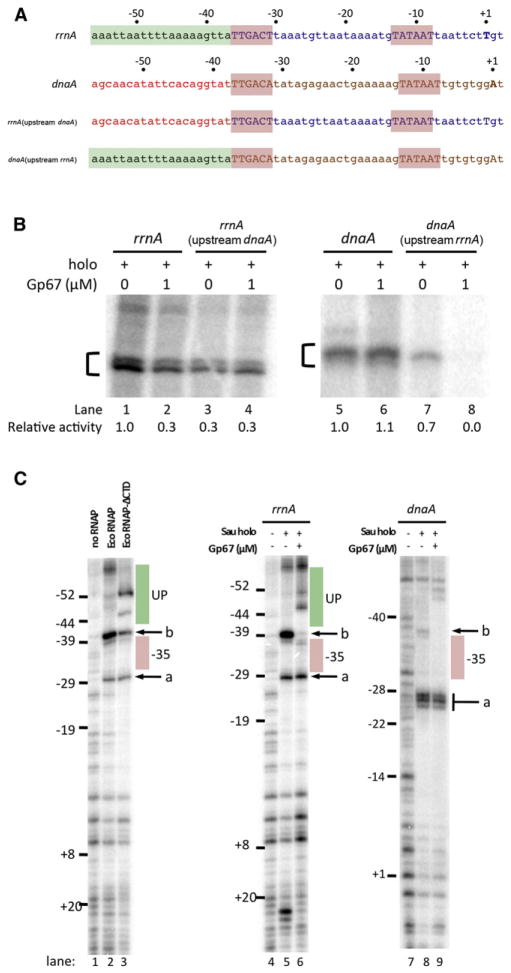
Figure 6. Gp67 Blocks UP-Element Utilization.
(A) Schematic of promoters used in swapping and footprinting experiments. DNA positions for the rrnA and dnaA promoters are labeled relative to the start site (+1). The –10 and –35 elements are shaded red. The putative UP-element region of the rrnA promoter is shaded green. The corresponding region of the dnaA promoter is denoted by red text.
(B) The region upstream of the –35 element is required for gp67 inhibition. In vitro transcription assays were performed from hybrid promoters constructed by swapping the region upstream of the –35 element between the rrnA (gp67-sensitive) and dnaA (gp67-resistant) promoters.
(C) DNase I footprinting. Left panel: Sau rrnA promoter with Eco RNAP and Eco RNAP-ΔαCTD. Middle panel: Sau rrnA promoter with Sau RNAP holoenzyme (±gp67). Right panel: Sau dnaA promoter with Sau RNAP holoenzyme (±gp67).
See also Figure S5.