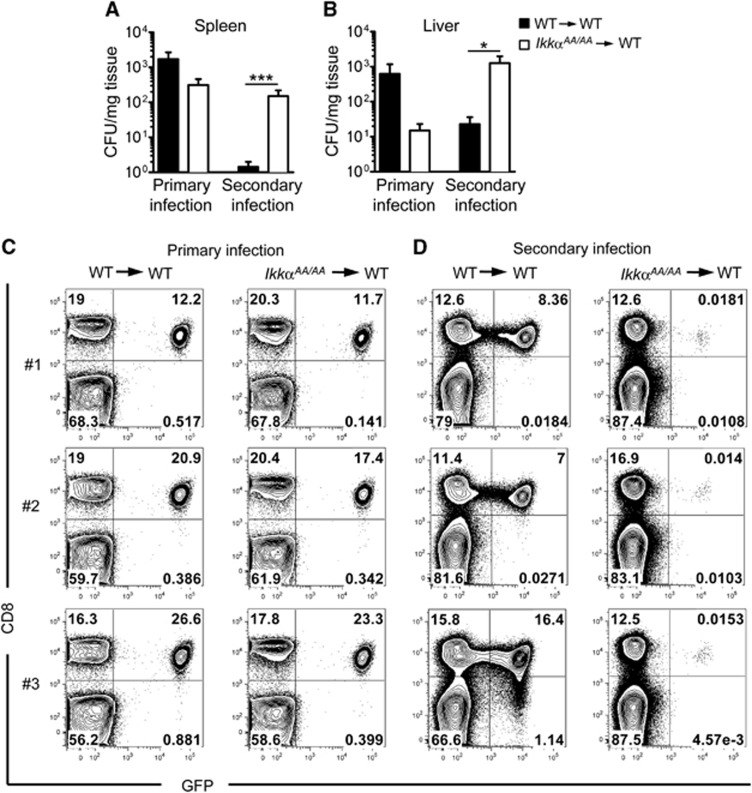
Figure 2.
IKKα is required for acquired immunity to L. monocytogenes and CD8+ T-cell memory. WT and IkkαAA/AA chimeric mice were infected intravenously (i.v.) with 104 CFU L. monocytogenes expressing chicken ovalbumin (Lm-OVA), spleens (A) and liver (B) were collected after 7 days for CFU measurements (primary infection). In parallel experiments, mice received a second infection with 106 CFU Lm-OVA 35 days after primary infection and CFU was determined in spleen and liver after a further 5 days (secondary infection). Data are represented as mean±s.e.m. of n=8–16, statistical analysis was performed with Mann–Whitney test; *P≤0.05, ***P≤0.001. (C) 104 CD8+ OT-I.EGFP cells were adoptively transferred to WT and IkkαAA/AA chimeric mice prior to infection with Lm-OVA (104 CFU i.v.), expansion of OVA-specific OT-I cells was measured by FACS analysis of spleens 7 days post infection (primary infection; C). In parallel experiments, mice received a second infection with 106 CFU Lm-OVA after 35 days, spleens were collected after a further 5 days for FACS analysis of OT-I cells (secondary infection; D). Representative data are shown from n=6 mice.