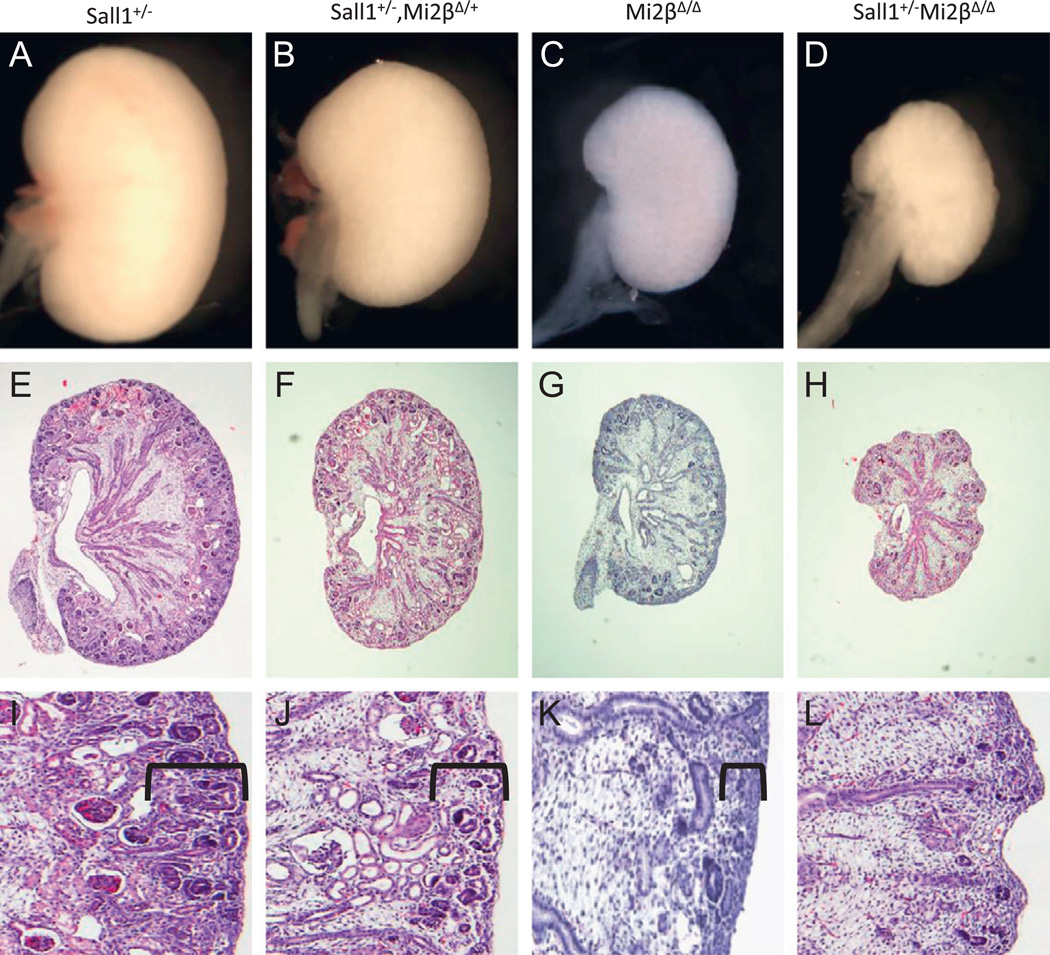
Fig. 8.
Sall1 and Mi2β genetically interact during embryonic kidney development. (A–D) E15.5 kidneys dissected from genetic crosses between Sall1+/−, Mi2βfl/+ and Six2-Cretg/+, Mi2βfl/+. Renal hypoplasia was seen in Sall1+/−/Mi2βΔ/+ double heterozygotes (B) and even more prominently in Mi2βΔ/Δ (C) and Sall1+/−, Mi2βΔ/Δ (D) compared to Sall1+/− (A) and wild type (data not shown) mice. (E–L) Histological analysis of Sall1/Mi2β compound mutants. Thickness of the nephrogenic zone (bracket) was reduced in Sall1+/−/ Mi2βΔ/+ double heterozygous kidneys (F, J); The loss of nephrogenic zone in Mi2βΔ/Δ kidneys was more severe (G, K). In Sall1+/−, Mi2βΔ/Δ mutant kidneys the nephrogenic zone was not detected at this stage and there were rare differentiated structures (H, L). Sall1+/− kidneys had a normal nephrogenic zone with many epithelial nephron precursor structures (E, I).