Figure 2. Individual probability of infection by the amphibian chytrid skin fungus in nature was strongly related to individual thermal history.
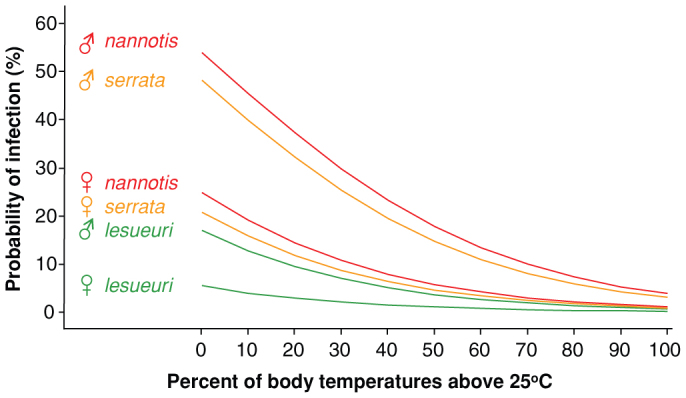
This logistic model, incorporating species identity, gender, and percent of body temperatures above 25°C (Table 2), was produced by averaging the three best fitted models, each with delta AICC < 3. Color coding corresponds to species-level susceptibility to epidemic chytridiomycosis (red most, amber intermediate, green least). Predictions of the model correspond well (r2 = 0.739, 4 d.f., P = 0.028) with population-level patterns of prevalence when it is used to predict prevalence by season and site, factors not included in the model.
