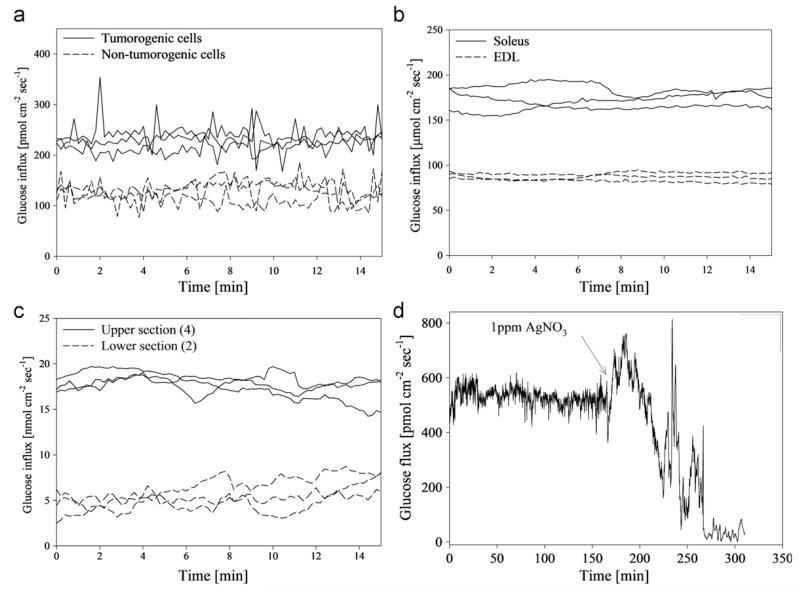
Fig. 2.
(a) Average glucose flux at the surface of tumorogenic and non-tumorogeinc human breast endothelial cells in αMEM (n=3). Glucose flux in cancerous cells was significantly higher than non-tumorogenic cells. (b) Average glucose flux at the surface of soleus and gastrocnemius muscle tissue from a mouse model (n=3). Glucose uptake in soleus tissue was significantly higher than gastrocnemius tissue for all preps. (c) Average glucose flux at the surface of upper jejunum and lower jejunum of excised mouse small intestinal tissue in RPMI media (n=3). Glucose flux in upper intestinal tissue was significantly higher than the lower intestine tissue. (d) Glucose flux into a mature (30 day old) Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm grown on a hollow fiber silicone membrane. (Reprinted with permission from (McLamore et al. 2011)).