Figure 6.
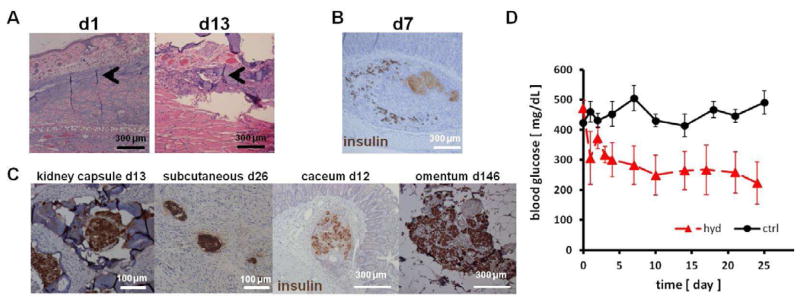
In vivo biocompatibility of hydrogel and islet function. (A) H&E stained histological sections of the rat pinna after 1 and 13 days of hydrogel injection. Minimal cell infiltration was observed in a small area adjacent to hydrogel (arrowheads). (B) Viable islets were scattered around the large mass of necrosis (light brown) observed after naked islets were injected under the submucosa of the stomach. (C) When transplanted with hydrogel, sygeneic islets stained positive for insulin (brown) were detected in various extrahepatic sites. (D) Blood glucose levels of diabetic rats after islet transplantation. 500 SP hydrogel encapsulated syngeneic islets were placed in an omentum pouch on day 0 (hyd, n=4). Controls were transplanted without the hydrogel (ctrl, n=5). Islet in hydrogel lowered blood glucose levels more effectively than control islets (p<0.05).
