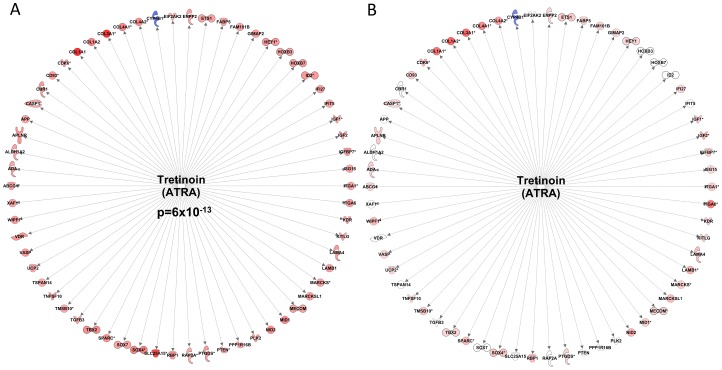
Figure 1. Resistance exercise training induces an all-trans retinoic acid differential gene expression signature that is common with endurance exercise training.
A) Forty-four subjects completed a 20 wk supervised resistance exercise training program (RET) and biopsy RNA was profiled before and 72 hr after training. Following SAM analysis of the 38 subjects that demonstrated a clear physiological gain, the gene list was uploaded to the Ingenuity Pathway Analysis database (IPA) and the up-stream regulators were identified using IPA's new up-stream tool. An All-trans-retinoic acid (Tretinoin) gene expression literature network was found to have a significant overlap with the RET dataset (p = 6×10−13). Furthermore, the direction changes of the common transcripts were sufficiently similar enough to conclude that ATRA like activity was increased (Z-score = 4.5). B) We re-evaluated our earlier RNA responses to endurance exercise training (EET) study which involved biopsy profiles before and after 6 weeks endurance training in 24 subjects [29], using the IPA tool and while the ATRA was not independently significant the vast majority of the genes within the RET ATRA signature were regulated in an identical manner by EET.