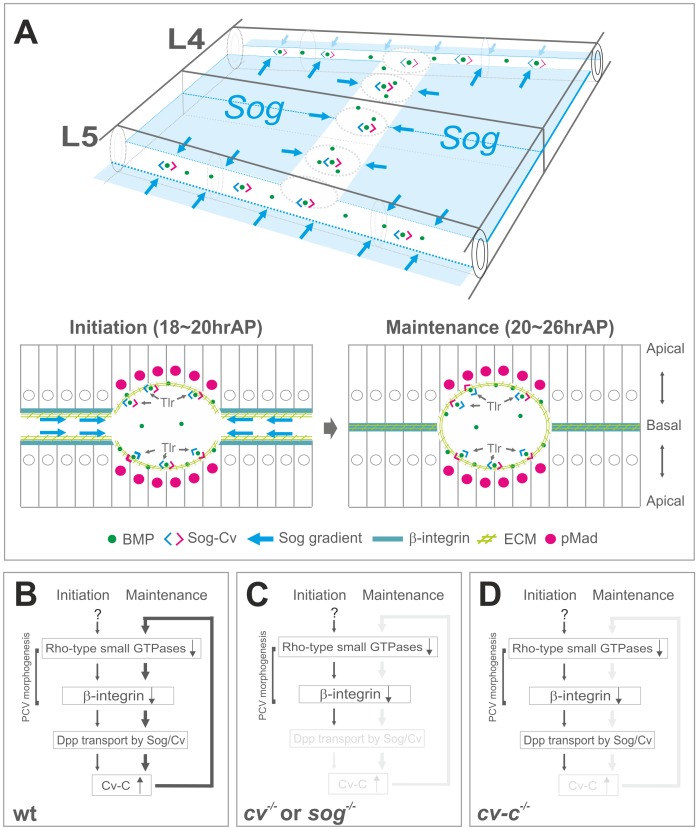
Figure 8. A model of coupling of BMP transport and PCV morphogenesis.
(A) Schematic overview of BMP transport and cross-section in the PCV region. BMP transport appears to occur through the ECM along PCV morphogenesis. (B) In wild-type pupal wing, the initial PCV morphogenesis is induced by inactivation of Rho-type small GTPases independently of BMP signaling. BMP transport is then guided toward the PCV region through low ß-integrin activity (∼18 hr AP). BMP signaling induces RhoGAP Cv-C to maintain PCV morphogenesis and BMP transport through a feed-forward loop (20∼26 hr AP). (C) In cv or sog pupal wing, the initial PCV morphogenesis occurs but is not maintained, due to the absence of BMP transport. (D) In cv-c pupal wing, BMP signaling and PCV morphogenesis are not maintained without a feed-forward loop.