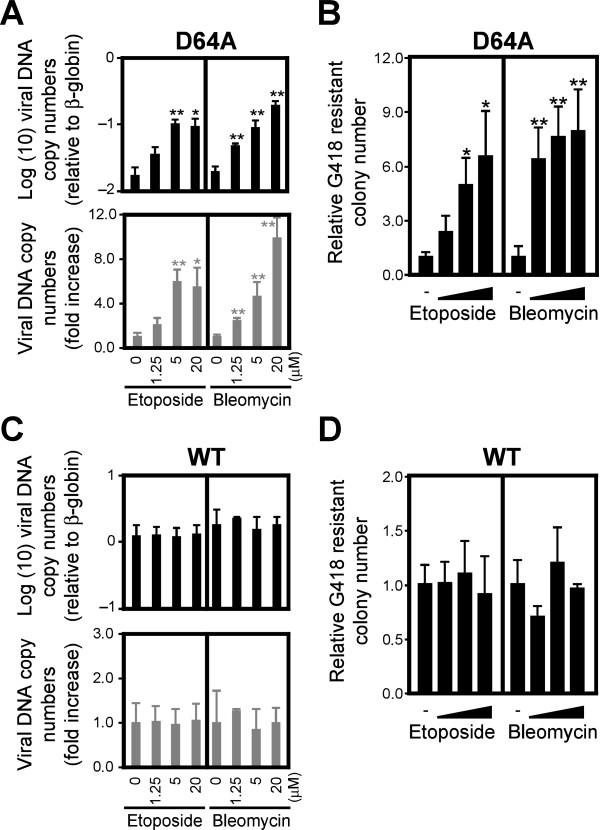
Figure 4.
DNA damage enhances the integration rate of HIV-1. Serum-starved HT1080 cells were infected with D64A (A) or WT (C) viruses in the presence of etoposide or bleomycin from 0–24 hpi. After 48 h, genomic DNA was extracted and subjected to qPCR. Relative copy numbers of HIV-1 DNA to β-globin were estimated (top) and the fold increase of HIV-1 DNA copy number compared to control infection that was conducted without DNA damaging agents (bottom) were calculated. For colony formation assay, VSVG-pseudotyped D64A (NL-Neo-IN-D64A-E(−)R(−)) (B) or WT (NL-Neo-E(−)R(−)) (D) viruses, which had the neomycin resistant gene (NeoR), were used. HT1080 cells were treated with various doses of etoposide or bleomycin for 24 h, which were added at the same time of viral infection. After selection with 600 μg/mL of G418, numbers of NeoR colonies were counted. Numbers of NeoR colonies were normalized by plating efficiency. Error bars, s.d. of triplicate assays. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01.