Figure 4.
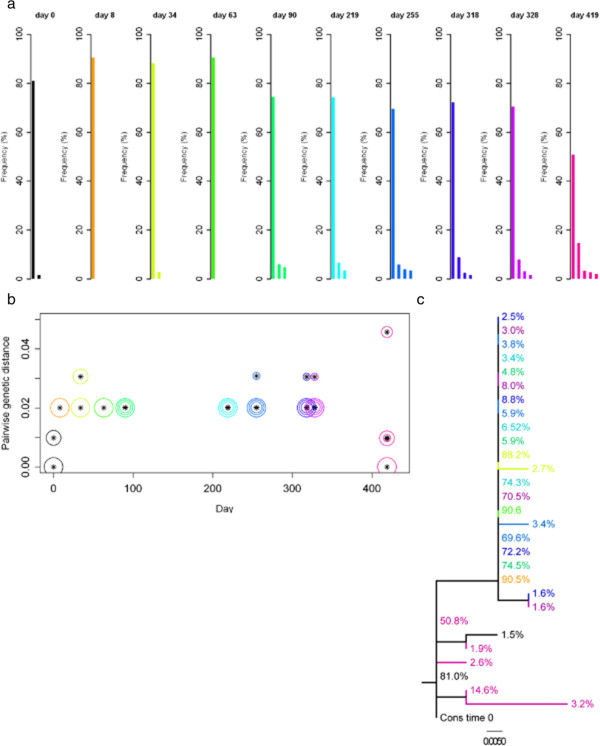
Sequence variants of the env V3, divergence and Neighbor-joining tree for subject 26. Samples over a time of ~ 60 weeks were analysed; with day 0 shown in black, and a rainbow colour scheme ranging from orange to pink applied to the remaining time points. (a) Sequence variants of the env V3. Each bar stands for one unique sequence variant. Only variants with frequencies above the 1.5% cut-off are displayed. (b) Divergence of env V3 sequence variants. Divergence is shown as the pairwise genetic distance (number of nucleotide substitutions per site) of a sequence variant at a given time from the consensus sequence at time 0. Genetic distances were estimated under the General Time Reversible model of nucleotide substitution, with proportion of invariable sites and gamma-distributed rate heterogeneity (GTR + I + G). Sizes of the circles around the symbols represent the frequencies of the sequence variants. The largest circle at each time point marks the major variant; the 2nd, 3rd and 4th most abundant variants are shown with gradually smaller circles; from the 5th most abundant variant circles have the same size. Note that the scale of the y-axis in this figure is different from Figures 5 and 6. (c) Neighbor-joining tree of env V3 sequence variants. The tree was reconstructed under the GTR + I + G model of nucleotide substitution. Branches are labeled with frequencies of sequence variants as depicted in (a). The scale bar represents the number of nucleotide substitutions per site.
