Abstract
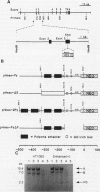
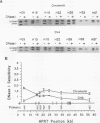
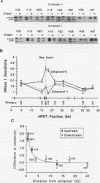
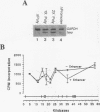
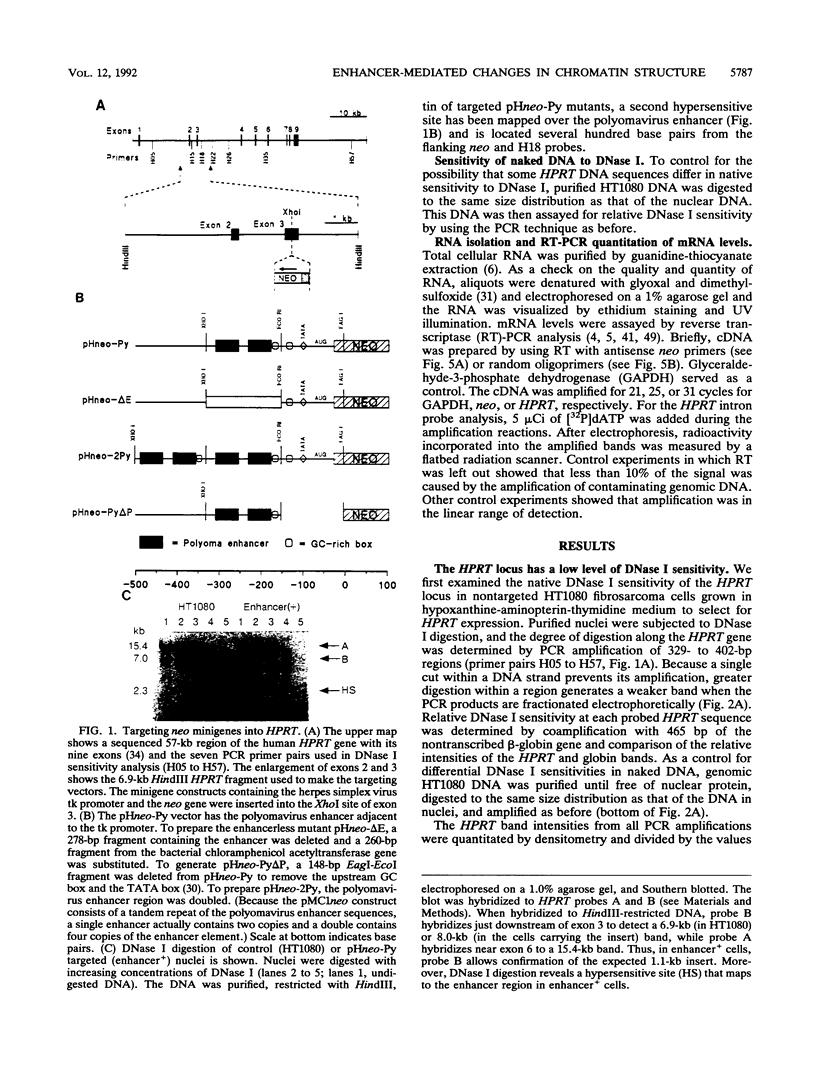
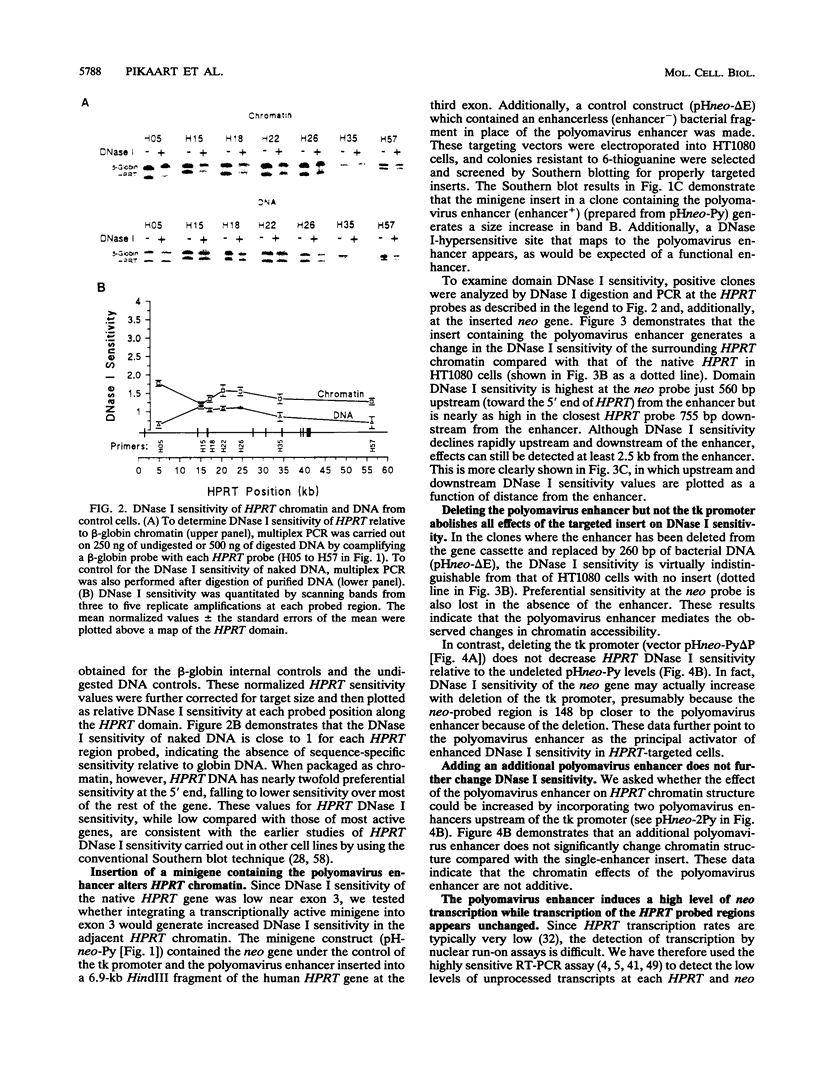
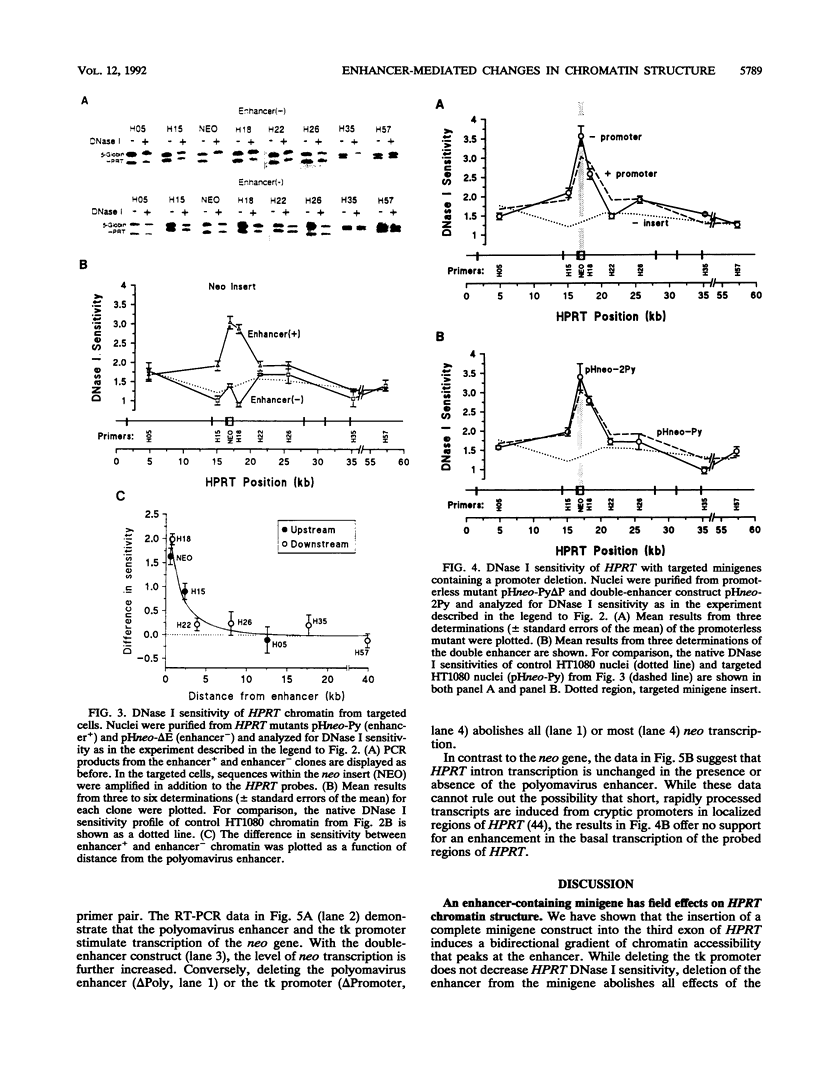
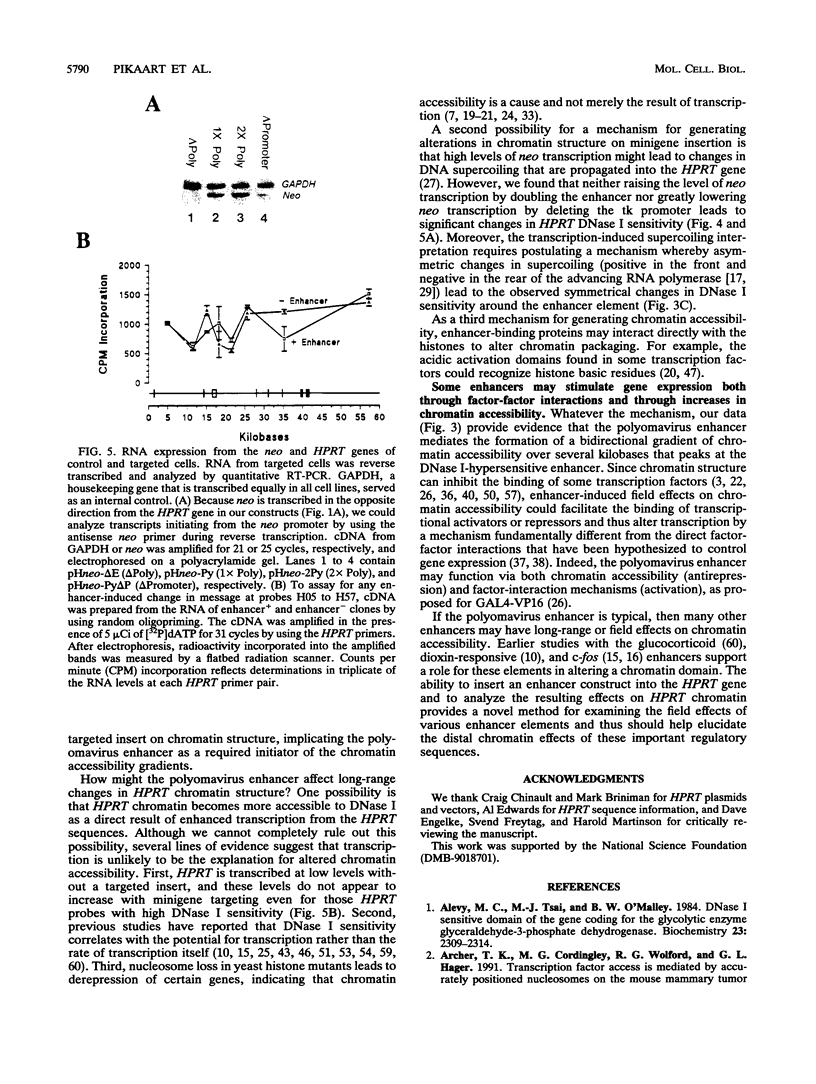
Recent studies suggest that enhancers may increase the accessibility of chromatin to transcription factors. To test the effects of a viral enhancer on chromatin accessibility, we have inserted minigenes with or without the polyomavirus enhancer into the third exon of the hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase (HPRT) gene by homologous recombination and have prepared high-resolution maps of gene accessibility by using a novel polymerase chain reaction assay for DNase I sensitivity. In its native state, we find that the HPRT gene has low sensitivity to DNase I in fibrosarcoma cells. Insertion of the polyomavirus enhancer and neo reporter gene into exon 3 confers altered HPRT DNase I sensitivity for several kilobases on either side of the enhancer. The changes in DNase I sensitivity peak near the enhancer and decline with distance from the enhancer. The increase in HPRT DNase I sensitivity persisted when the tk promoter was deleted from the inserted construct but disappeared when the enhancer was deleted. These experiments identify the polyomavirus enhancer as a cis-acting initiator of chromatin accessibility.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alevy M. C., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. DNase I sensitive domain of the gene coding for the glycolytic enzyme glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Biochemistry. 1984 May 8;23(10):2309–2314. doi: 10.1021/bi00305a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archer T. K., Cordingley M. G., Wolford R. G., Hager G. L. Transcription factor access is mediated by accurately positioned nucleosomes on the mouse mammary tumor virus promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):688–698. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker-André M., Hahlbrock K. Absolute mRNA quantification using the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). A novel approach by a PCR aided transcript titration assay (PATTY). Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 25;17(22):9437–9446. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.22.9437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker P. B., Ruppert S., Schütz G. Genomic footprinting reveals cell type-specific DNA binding of ubiquitous factors. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):435–443. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90639-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chelly J., Kaplan J. C., Maire P., Gautron S., Kahn A. Transcription of the dystrophin gene in human muscle and non-muscle tissue. Nature. 1988 Jun 30;333(6176):858–860. doi: 10.1038/333858a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark-Adams C. D., Norris D., Osley M. A., Fassler J. S., Winston F. Changes in histone gene dosage alter transcription in yeast. Genes Dev. 1988 Feb;2(2):150–159. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.2.150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark-Adams C. D., Norris D., Osley M. A., Fassler J. S., Winston F. Changes in histone gene dosage alter transcription in yeast. Genes Dev. 1988 Feb;2(2):150–159. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.2.150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corthésy B., Léonnard P., Wahli W. Transcriptional potentiation of the vitellogenin B1 promoter by a combination of both nucleosome assembly and transcription factors: an in vitro dissection. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):3926–3933. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.3926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croston G. E., Kerrigan L. A., Lira L. M., Marshak D. R., Kadonaga J. T. Sequence-specific antirepression of histone H1-mediated inhibition of basal RNA polymerase II transcription. Science. 1991 Feb 8;251(4994):643–649. doi: 10.1126/science.1899487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durrin L. K., Whitlock J. P., Jr 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin-inducible aryl hydrocarbon receptor-mediated change in CYP1A1 chromatin structure occurs independently of transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;9(12):5733–5737. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.12.5733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elgin S. C. The formation and function of DNase I hypersensitive sites in the process of gene activation. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 25;263(36):19259–19262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson B. M., Felsenfeld G. Specific factor conferring nuclease hypersensitivity at the 5' end of the chicken adult beta-globin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):95–99. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felts S. J., Weil P. A., Chalkley R. Transcription factor requirements for in vitro formation of transcriptionally competent 5S rRNA gene chromatin. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):2390–2401. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.2390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng J. L., Irving J., Villeponteau B. A phosphatase inhibitor enhances the DNase I sensitivity of active chromatin. Biochemistry. 1991 May 14;30(19):4747–4752. doi: 10.1021/bi00233a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng J. L., Villeponteau B. Serum stimulation of the c-fos enhancer induces reversible changes in c-fos chromatin structure. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):1126–1133. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.1126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng J., Villeponteau B. High-resolution analysis of c-fos chromatin accessibility using a novel DNase I-PCR assay. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Apr 6;1130(3):253–258. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(92)90437-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giaever G. N., Wang J. C. Supercoiling of intracellular DNA can occur in eukaryotic cells. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):849–856. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90140-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross D. S., Garrard W. T. Nuclease hypersensitive sites in chromatin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:159–197. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M. Histone function in transcription. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1990;6:643–678. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.06.110190.003235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han M., Grunstein M. Nucleosome loss activates yeast downstream promoters in vivo. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):1137–1145. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90258-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han M., Kim U. J., Kayne P., Grunstein M. Depletion of histone H4 and nucleosomes activates the PHO5 gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2221–2228. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03061.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ip Y. T., Fournier R. E., Chalkley R. Extinction of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene expression is associated with loss of a specific chromatin-binding protein from a far upstream domain. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3782–3787. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jantzen K., Fritton H. P., Igo-Kemenes T. The DNase I sensitive domain of the chicken lysozyme gene spans 24 kb. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 11;14(15):6085–6099. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.15.6085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kayne P. S., Kim U. J., Han M., Mullen J. R., Yoshizaki F., Grunstein M. Extremely conserved histone H4 N terminus is dispensable for growth but essential for repressing the silent mating loci in yeast. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):27–39. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90006-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson G. M., Knoll B. J., March C. J., Woo S. L., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Definition of 5' and 3' structural boundaries of the chromatin domain containing the ovalbumin multigene family. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 10;257(3):1501–1507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laybourn P. J., Kadonaga J. T. Role of nucleosomal cores and histone H1 in regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Science. 1991 Oct 11;254(5029):238–245. doi: 10.1126/science.254.5029.238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. S., Garrard W. T. Transcription-induced nucleosome 'splitting': an underlying structure for DNase I sensitive chromatin. EMBO J. 1991 Mar;10(3):607–615. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07988.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin D., Chinault A. C. Comparative study of DNase I sensitivity at the X-linked human HPRT locus. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1988 May;14(3):261–272. doi: 10.1007/BF01534587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. F., Wang J. C. Supercoiling of the DNA template during transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7024–7027. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Kingsbury R. Transcriptional control signals of a eukaryotic protein-coding gene. Science. 1982 Jul 23;217(4557):316–324. doi: 10.1126/science.6283634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Carmichael G. G. Analysis of single- and double-stranded nucleic acids on polyacrylamide and agarose gels by using glyoxal and acridine orange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4835–4838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. W., Konecki D. S., Brennand J., Caskey C. T. Structure, expression, and mutation of the hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2147–2151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel P. I., Framson P. E., Caskey C. T., Chinault A. C. Fine structure of the human hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):393–403. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pederson D. S., Thoma F., Simpson R. T. Core particle, fiber, and transcriptionally active chromatin structure. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:117–147. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.001001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piña B., Brüggemeier U., Beato M. Nucleosome positioning modulates accessibility of regulatory proteins to the mouse mammary tumor virus promoter. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):719–731. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90087-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M., Gann A. A. Activators and targets. Nature. 1990 Jul 26;346(6282):329–331. doi: 10.1038/346329a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. How eukaryotic transcriptional activators work. Nature. 1988 Oct 20;335(6192):683–689. doi: 10.1038/335683a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rappolee D. A., Mark D., Banda M. J., Werb Z. Wound macrophages express TGF-alpha and other growth factors in vivo: analysis by mRNA phenotyping. Science. 1988 Aug 5;241(4866):708–712. doi: 10.1126/science.3041594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reik A., Schütz G., Stewart A. F. Glucocorticoids are required for establishment and maintenance of an alteration in chromatin structure: induction leads to a reversible disruption of nucleosomes over an enhancer. EMBO J. 1991 Sep;10(9):2569–2576. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07797.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rupp R. A., Weintraub H. Ubiquitous MyoD transcription at the midblastula transition precedes induction-dependent MyoD expression in presumptive mesoderm of X. laevis. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):927–937. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90545-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalder J., Groudine M., Dodgson J. B., Engel J. D., Weintraub H. Hb switching in chickens. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):973–980. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90088-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su L. K., Kadesch T. The immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer functions as the promoter for I mu sterile transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2619–2624. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas K. R., Capecchi M. R. Site-directed mutagenesis by gene targeting in mouse embryo-derived stem cells. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):503–512. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90646-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villeponteau B., Martinson H. G. Gamma rays and bleomycin nick DNA and reverse the DNase I sensitivity of beta-globin gene chromatin in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1917–1924. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. M., Doyle M. V., Mark D. F. Quantitation of mRNA by the polymerase chain reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9717–9721. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H. Assembly and propagation of repressed and depressed chromosomal states. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):705–711. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90267-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolffe A. P., Brown D. D. Developmental regulation of two 5S ribosomal RNA genes. Science. 1988 Sep 23;241(4873):1626–1632. doi: 10.1126/science.241.4873.1626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolffe A. P. Dominant and specific repression of Xenopus oocyte 5S RNA genes and satellite I DNA by histone H1. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):527–537. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03407.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood W. I., Felsenfeld G. Chromatin structure of the chicken beta-globin gene region. Sensitivity to DNase I, micrococcal nuclease, and DNase II. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7730–7736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Workman J. L., Abmayr S. M., Cromlish W. A., Roeder R. G. Transcriptional regulation by the immediate early protein of pseudorabies virus during in vitro nucleosome assembly. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):211–219. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90044-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Workman J. L., Roeder R. G., Kingston R. E. An upstream transcription factor, USF (MLTF), facilitates the formation of preinitiation complexes during in vitro chromatin assembly. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1299–1308. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08239.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Workman J. L., Taylor I. C., Kingston R. E. Activation domains of stably bound GAL4 derivatives alleviate repression of promoters by nucleosomes. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):533–544. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90237-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang T. P., Caskey C. T. Nuclease sensitivity of the mouse HPRT gene promoter region: differential sensitivity on the active and inactive X chromosomes. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2994–2998. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaniv M., Cereghini S. Structure of transcriptionally active chromatin. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1986;21(1):1–26. doi: 10.3109/10409238609113607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaret K. S., Yamamoto K. R. Reversible and persistent changes in chromatin structure accompany activation of a glucocorticoid-dependent enhancer element. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):29–38. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90523-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]