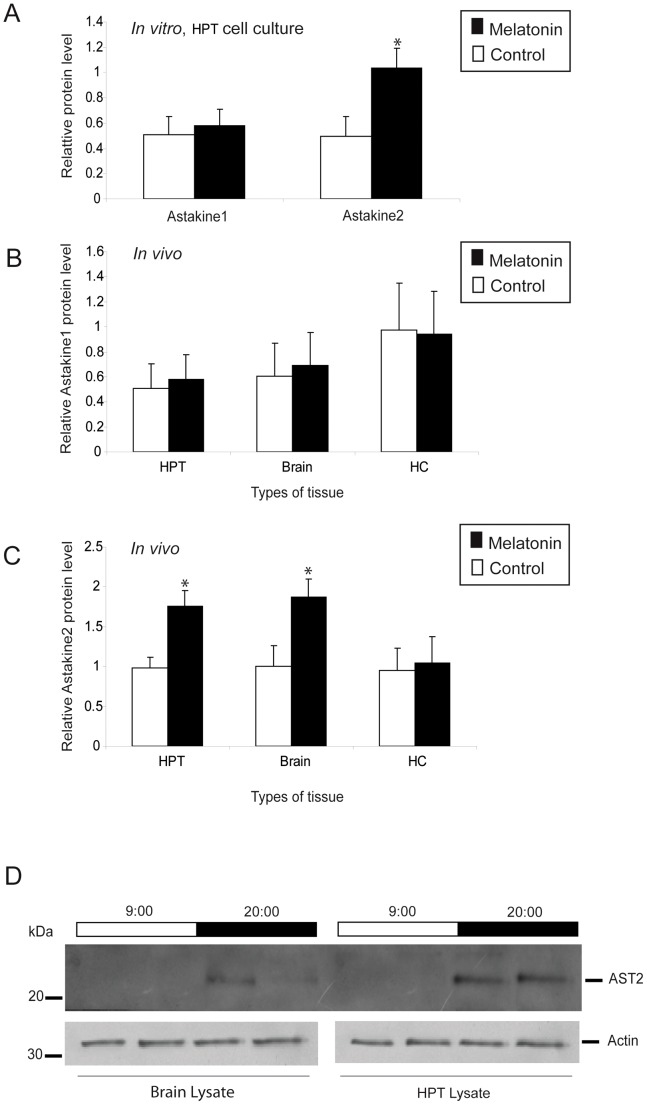
Figure 2. Melatonin induces higher AST2 protein levels in vitro and in vivo.
A) Relative levels of AST1 or AST2 protein in cultured HPT cells in vitro as estimated by ELISA, after incubation with melatonin. Black bars = melatonin (3 µM), white bars = control. The level of β-actin was used as an internal control. B) Relative levels of AST1 in the HPT, brain and hemocytes in live crayfish as estimated by ELISA, after injection of melatonin. Black bars = melatonin (4.3 nmol/g), white bars = control. The level of β-actin was used as an internal control. C) Relative levels of AST2 in the HPT, brain and hemocytes in live crayfish as estimated by ELISA, after injection of melatonin. Black bars = melatonin (4.3 nmol/g), white bars = control. The level of β-actin was used as an internal control. The asterisks indicate significant differences (*P<0.05); one-way ANOVA with Duncan's new multiple-range test and the Tukey test. Results are representative of three independent experiments. Error bars indicate SD from three replicates and the experiment has been repeated three times with similar results. D) Western blot analysis of AST2 in the brain and HPT at 9:00 and 20:00, using an antibody against AST2. The expression level of actin was used as an internal control. Light and dark periods are indicated on the top of the blot.