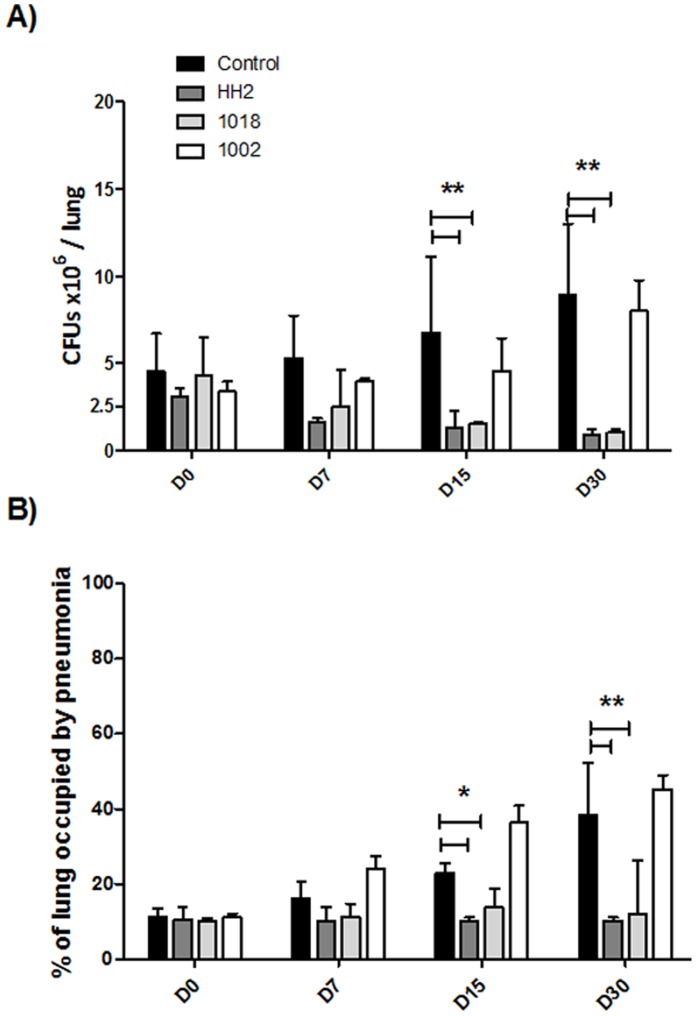
Figure 4. Effect of antimicrobial peptide treatment on pulmonary bacilli burdens and tissue damage (pneumonia) during experimental tuberculosis kinetic.
(A) Mice were infected with the drug-sensitive H37Rv Mtb strain, and after 60 days were treated, three times per week, with ∼1 mg/kg of the indicated peptide in 100 mL of saline solution. HH2 and 1018 decreased the lung bacillary loads in comparison with untreated mice, whereas 1002 showed no significant changes. (B) Percentage of the lung surface affected by pneumonia as determined by automated morphometry. Results are expressed as means ± standard deviations, P<0.05 * or P<0.01** were considered statistically significant. Both 1018 and HH2 peptides significantly decreased the pneumonic area when compared with the control group. The graph is representative data from a series of 3 independent experiments.