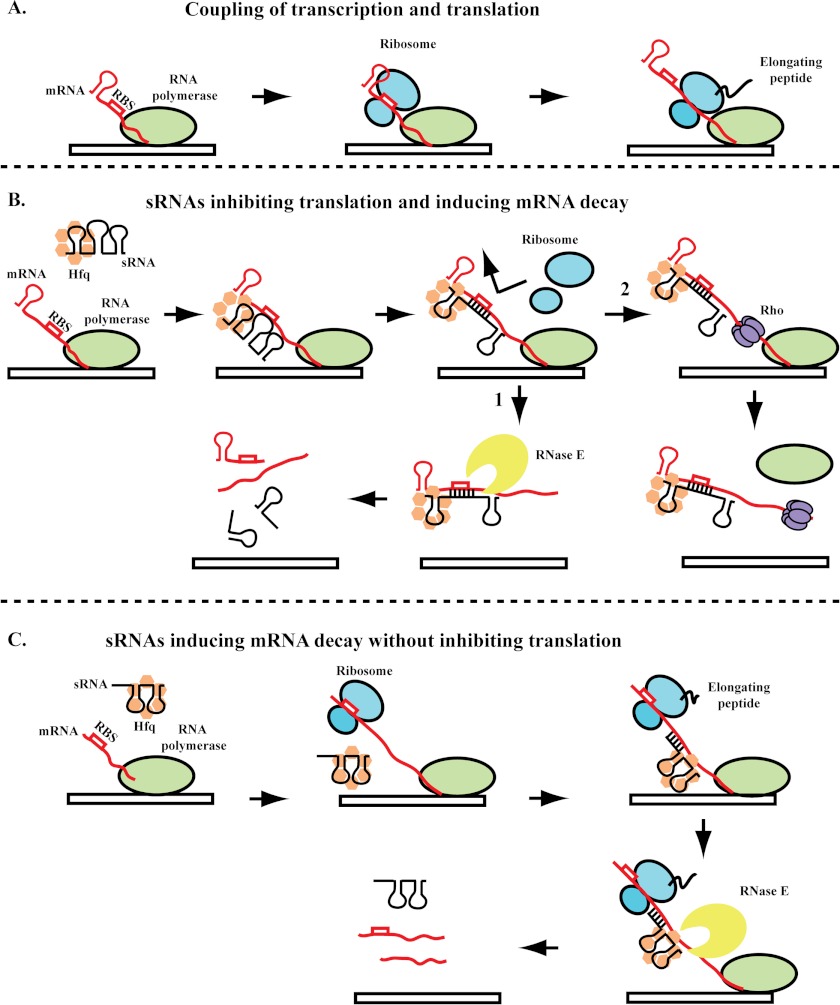
FIGURE 2.
Mechanisms of sRNA-mediated regulation. A, the coupling of transcription by RNA polymerase (green) and translation by the ribosome (blue) in the absence of sRNA regulation. Growing evidence suggests the possibility of interactions between RNA polymerase and the ribosome to ensure coupling (see text). B, sRNAs can block ribosome entry by pairing with sequences at or near the RBS of the mRNA. Pairing of the sRNA with the target mRNA is facilitated by Hfq (orange). As a result of blocking ribosome binding, the sRNA can decouple transcription and translation. Arrow 1, the unprotected mRNA may then be subject to cleavage by RNase E (yellow). Arrow 2, in addition to access to RNase E, the untranslated RNA can also provide a binding site for Rho (purple), leading to transcription termination. C, alternatively, sRNAs may induce cleavage of the mRNA by recruiting RNase E, causing mRNA cleavage without inhibiting translation. Recruitment of RNase E may be through interactions with Hfq, the RNAs, or both.