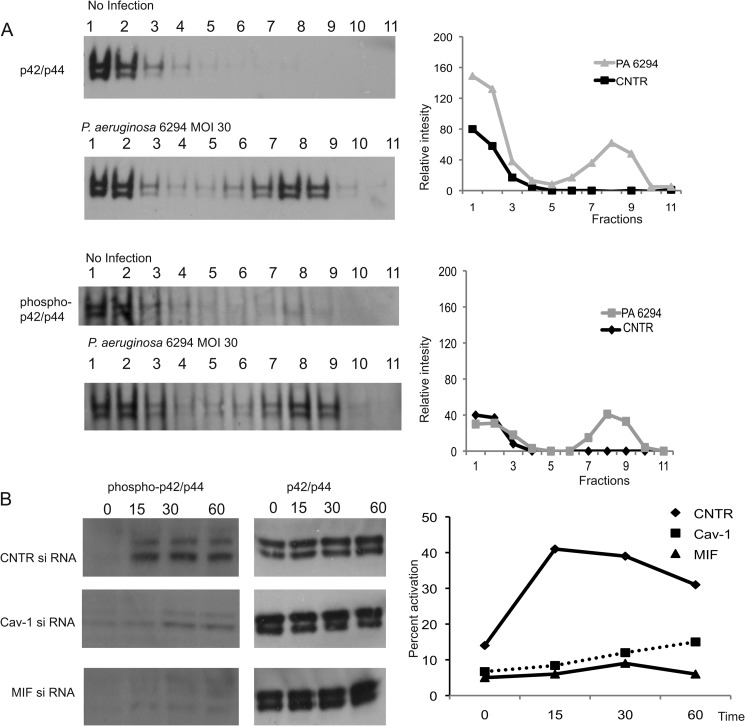
FIGURE 7.
Down-regulating caveolin-1 levels in HPCEC ablates MAPK p42/p44-dependent signaling. A, P. aeruginosa infection stimulated MAPK p42/p44 rapid recruitment to lipid rafts in caveolin-1-sufficient cells. HPCEC were infected with P. aeruginosa 6294 strain for 20 min, and lipid raft fractionations were carried out. Samples were analyzed for MAPK p42/p44 partitioning by Western blotting (top two panels). MAPK p42/p44 activation was detected by probing with phospho-specific p42/p44 Ab (bottom two panels). Western blot images were analyzed by densitometry and the presence of MAPK p42/p44 compared by measuring the intensity of the individual bands within the individual lanes. The graphs present relative intensities of the bands for the individual fractions. B, reducing MIF or caveolin-1 levels resulted in a decrease of MAPK p42/p44 activation elicited by P. aeruginosa 6294 infection. HPCEC were treated with control siRNA (CNTR), MIF-specific siRNA, or caveolin-1 (Cav-1)-specific siRNA, infected with P. aeruginosa strain 6294 at multiplicity of infection 30, total cellular lysates were prepared by lysis in radioimmune precipitation assay buffer at 15, 30, or 60 min post-infection. Equal levels of total protein were loaded onto 4–12% NuPAGE and analyzed for phospho-p42/p44 by Western blotting. The Western blot images were analyzed by densitometry, and the percent activation of MAPK p42/p44 was plotted as a function of time. MOI, multiplicity of infection.