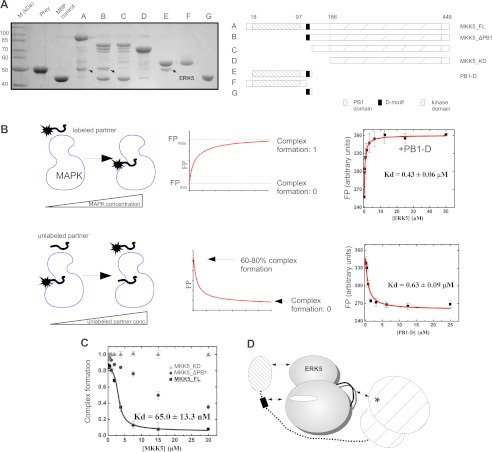
FIGURE 2.
Characterization of the MKK5-ERK5 interaction. A, three distinct MKK5 regions contribute to its interaction with ERK5. MBP pulldown results with the ERK5 kinase domain (residues 1–431) as prey and different deletion constructs (A, A–G panels) of MKK5 as baits. Interaction of bait and prey was detected on an SDS-PAGE gel stained with Coomassie protein dye. Arrows indicate the position of ERK5 in the pulldown experiments. MBP control was used as negative control to assess unspecific binding of the prey. Bands appearing in addition to baits or preys are degradation products of MBP-fusion proteins. The panel shows the results of a representative MBP pulldown assay from two independent experiments. B, schematic diagram of direct (top panels) and competitive (bottom panels) FP-based titration experiments for determining protein-peptide or protein-protein binding affinities (Kd). Panels on the right show binding isotherms for direct (on the top) and for competitive (on the bottom) ERK5·PB1-D binding experiments. Errors indicate uncertainty in the fit, and error bars on the binding isotherms show S.D. based on three independent measurements. C, competitive binding experiments to monitor binding of MKK5_KD, MKK5_ΔPB1, and MKK5_FL to ERK5. The panel shows the competitive binding curve using unlabeled PB1-D as the competitor and labeled ERK5·PB1-D complex as the reporter (PB1-D labeled with 5-iodoacetamidofluorescein, IAF). The y axis shows the degree of complex formation that was determined based on arbitrary FPmin and FPmax units from numerical fits to competitive binding equations as shown on B. Data were fit to a competition binding equation. Errors indicate uncertainty in the fit, and error bars on the binding isotherms show S.D. based on three independent measurements. D, interactions contributing to the formation of the MKK5·ERK5 binary complex: (i) the MKK5 PB1 domain binds to the ERK5 kinase domain, (ii) MKK5 D-motif presumably binds in the ERK5 docking groove, and (iii) the MKK5 kinase domain binds to the ERK5 kinase domain on an area distinct from the PB1 and D-motif-interacting surfaces. This latter interaction might speculatively form between the MKK5 active site and the ERK5 activation loop (shown with an asterisk or with a black line, respectively). conc., concentration.