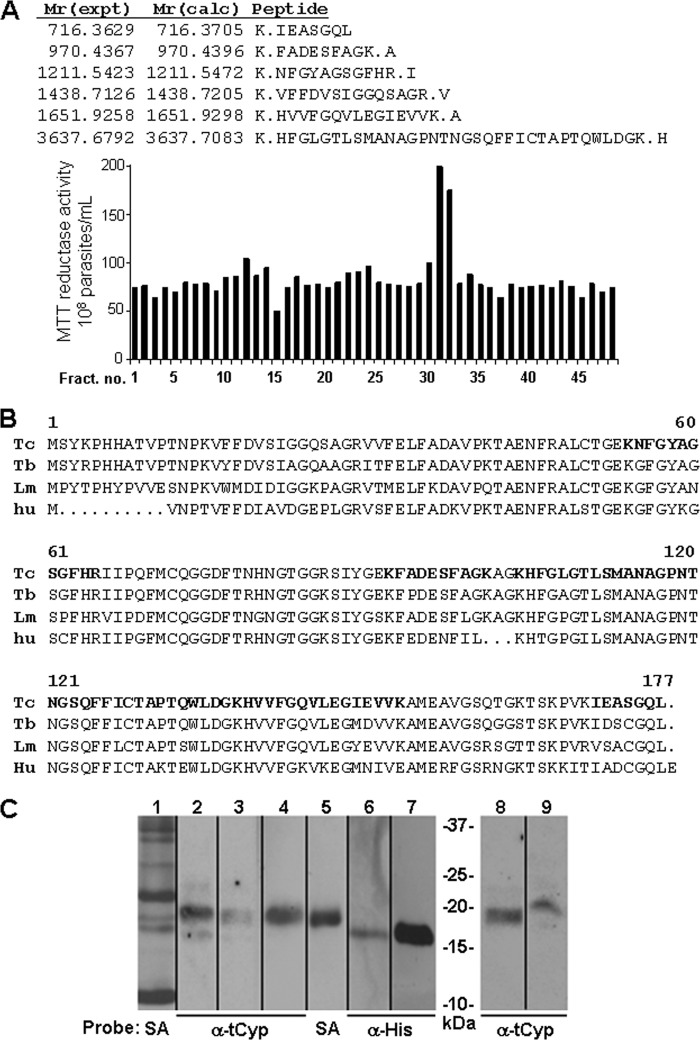
FIGURE 2.
Identification of secreted cyclophilin 19 in T. cruzi-conditioned medium. A, reverse-phase C-18 HPLC fractionation of conditioned medium identified fractions 32 and 33 containing proteins leading to enhanced parasite reductase activity. Mass spectrometry of unfractionated CM and the active HPLC fractions contained trypanosomal cyclophilin 19. B, shown is alignment of the cyclophilin 19 proteins from T. cruzi (Tc) (61), T. brucei (Tb) (14), and L. major (Lm) (25) with human cyclophilin A (hu). Bold residues correspond to the peptide sequences from the mass spectrometric data in panel A. C, Western blot analysis of trypanosomal and leishmanial cyclophilin 19. Lane 1, total secreted proteins of T. cruzi labeled with biotin and detected with streptavidin-horseradish peroxidase (HRP) (SA); Lanes 2 and 3, cell lysate and conditioned medium of T. cruzi (107 cells), respectively; lanes 4 and 5, pulldown of T. cruzi-conditioned medium-biotinylated proteins using immobilized-SA beads probed with trypanosomal cyclophilin 19 antibodies (α-tCyp) and streptavidin-HRP, respectively; lanes 6 and 7, immobilized magnetic P6-trialysin bead pulldown of recombinant tCyp19 and tCyp19 protein alone (1 μg used as control) probed with anti-His-tag antibodies (α-His), respectively; lanes 8 and 9, cell lysate and conditioned medium of L. amazonensis promastigotes (from 107 cells) probed with α-tCyp19 antibodies. Comparative densitometry analysis of signals from lanes 2 and 3 and of 8 and 9 indicate that the conditioned medium contains 25–30% of total cellular Cyp19.