Fig. 4. The pharmacological effects of ebselen are mediated by inositol depletion.
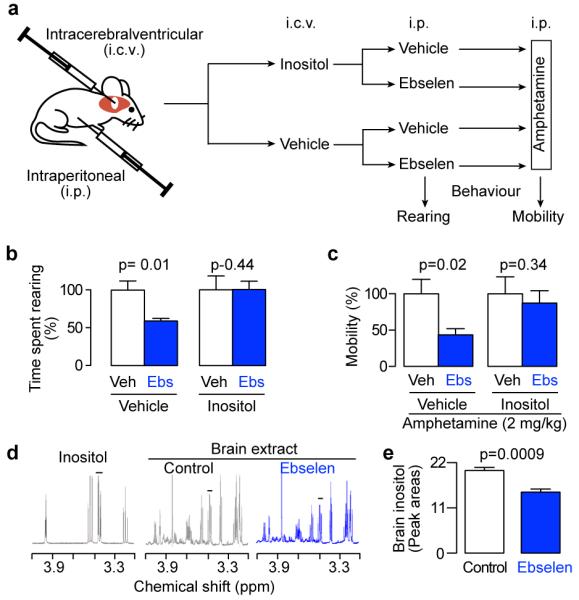
(a) Schematic outlining the experimental protocol used to investigate inositol reversal of behaviours induced by ebselen. Drugs were injected as follows: 1 μL of 0.5 M inositol, 5 mg/kg ebselen and 2 mg/kg amphetamine. (b) Effect of inositol on the ability of ebselen to attenuate rearing, analysed by pre-planned paired t-tests between ebselen and control, n=4-6. (c) Effect of inositol on the ability of ebselen to attenuate amphetamine-induced hyperactivity (mobility) analyzed by pre-planned paired t-tests between ebselen and control, n=5-6. (d) Proton NMR spectra of authentic inositol and brain extracts from mice injected intraperitoneally with either ebselen (10 mg/kg) or hydroxypropyl ß-cyclodextrin(4% w/v, Control). (e), Effect of ebselen (10 mg/kg) on inositol levels in mouse brain. Inositol was quantified by integration of the C1 and C3 peaks (indicated by the bar in d), and analyzed by a pre-planned one-way t-test between ebselen and control, n=4. All error bars represent standard error of the means.
