Figure 7.
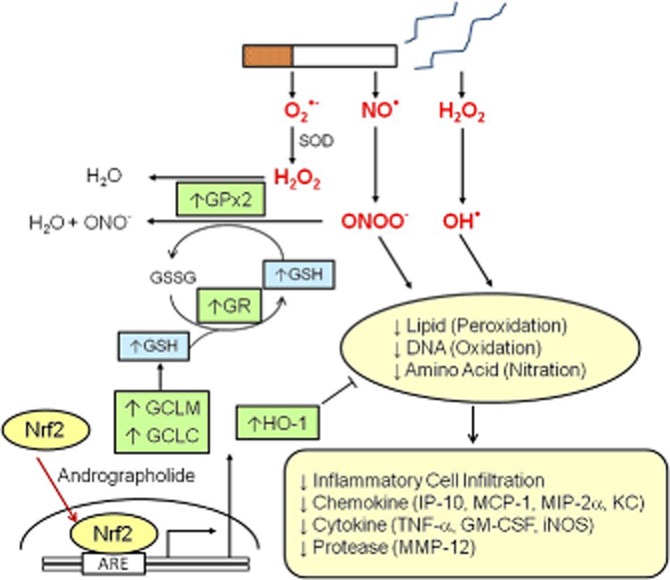
Summary of proposed antioxidant mechanisms of action of andrographolide in cigarette smoke-induced oxidative damage to the lungs. Cigarette smoke contains reactive oxygen and reactive nitrogen species such as NO•, superoxide anion (O2•−) and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), which can be transformed into more damaging free radicals such as hydroxide radical (OH•) or peroxynitrate (ONOO-), that will lead to lipid peroxidation, DNA oxidation and amino acid nitration. Oxidative damage induces expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, and subsequent pulmonary inflammatory cell infiltration. Andrographolide promotes Nrf2 nuclear translocation and binding to antioxidant response element (ARE) leading to up-regulation of antioxidants GCLM, GCLC, GPx-2, GR and HO-1, and subsequent production of GSH and removal of H2O2 and ONOO-. These actions contribute to the protective effects of andrographolide in cigarette smoke-induced lung injury.
