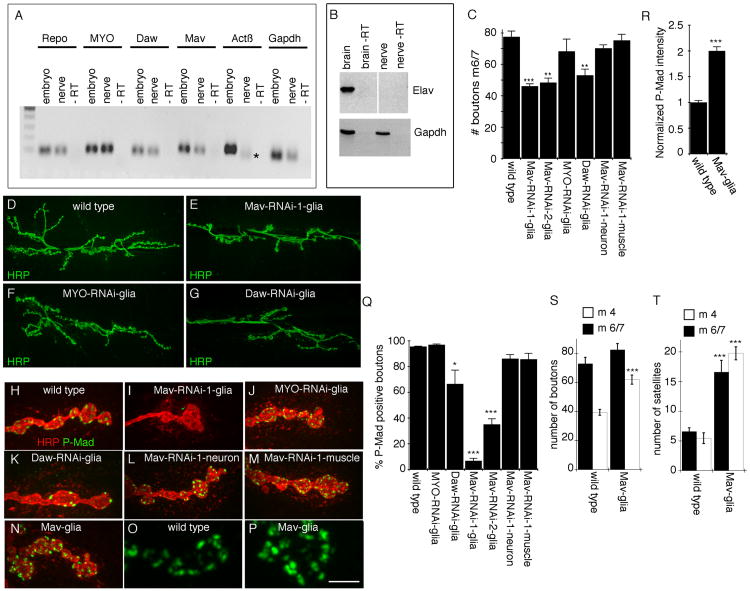
Figure 1. Glial Mav Regulates TGF-β Activation.
(A) Real-time PCR products from larval segmental nerve and embryonic RNA, showing that MYO, Daw, and Mav transcripts, but not Actβ transcripts, are detected in nerve glia. * indicates an unspecific product as determined by sequencing (n = 3).
(B) Reverse transcriptase PCR from larval brain and segmental nerve RNA, showing that the neuron-specific transcript elav is present in brain but not in segmental nerve RNA.
(C) Number of boutons at muscles 6 and 7 (segment A3) of third-instar larvae expressing Mav-RNAi, MYO-RNAi, or Daw-RNAi in NMJ glia (Gli-Gal4) and Mav-RNAi in neurons (C380-Gal4) or muscles (C57-Gal4), showing that downregulating Mav in NMJ glia reduces bouton number (from left to right, n = 22, 11, 14, 6, 9, 16, 17).
(D–G) Confocal images of third-instar larval NMJs labeled with anti-HRP in (D) wild-type control and animals expressing (E) Mav-RNAi, (F) MYO-RNAi, or (G) Daw-RNAi in NMJ glia.
(H–N) Confocal images of NMJ branches in preparations double labeled with anti-HRP and anti-P-Mad in (H) controls and (I–N) larvae expressing (I) Mav-RNAi, (J) MYO-RNAi, or (K) Daw-RNAi in glia; (L) Mav-RNAi in neurons (C380-Gal4); (M) Mav-RNAi in muscles (C57-Gal4); and (N) Mav in glia, showing that Mav downregulation in NMJ glia virtually eliminates P-Mad signal and that this signal is enhanced upon Mav overexpression in NMJ glia.
(O and P) High-magnification views of P-Mad staining at synaptic boutons in (O) control and (P) Mav overexpression in glia.
(Q) Percentage of P-Mad positive synaptic boutons in the indicated genotypes (from left to right, n = 18, 11, 14, 6, 12, 11, 12).
(R) Mean P-Mad signal intensity normalized to control in the indicated genotypes (n = 10 for each genotype).
(S and T) Quantification of the number of (S) boutons and (T) satellite boutons at abdominal segment 3 in muscles 6 and 7 (black bars) and 4 (white bars), in wild-type and Mav glia (from left to right, n = 12 and 17 in both S and T).
Error bars represent mean ± SEM (***p < 0.001, **p ≤ 0.01, *p ≤ 0.05). Scale bar represents 22 μm for (D)–(G), 4 μm for (H)–(N), and 2.5 μm for (O) and (P).