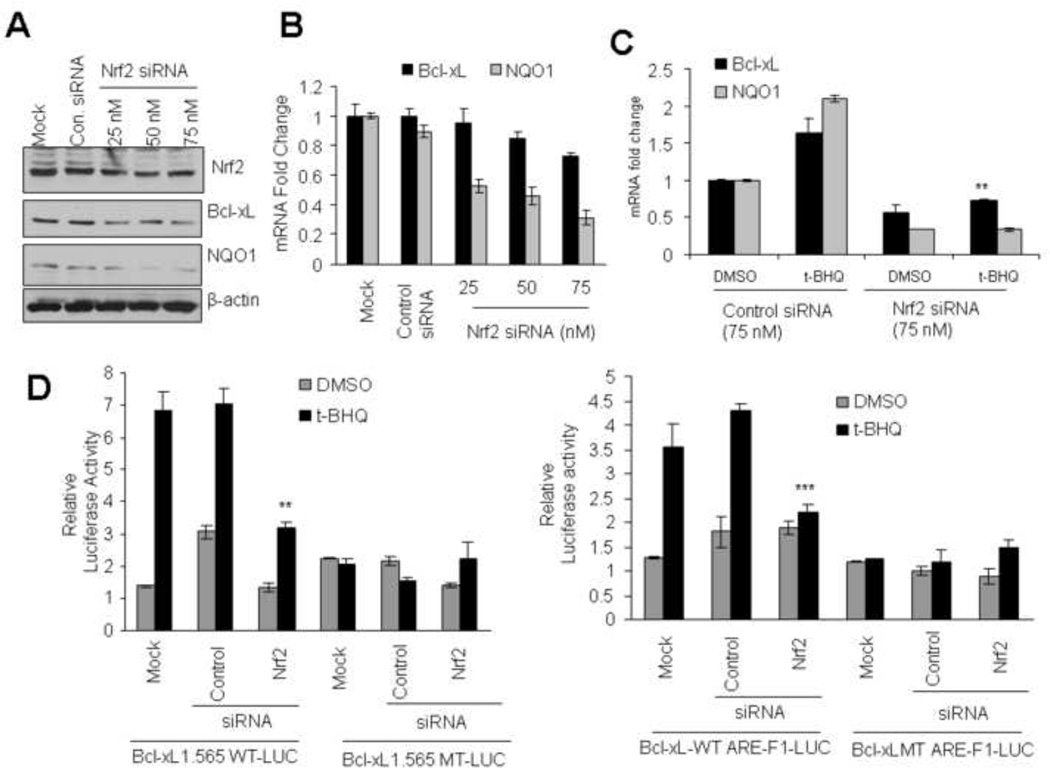
Fig. 5.
siRNA inhibition of Nrf2 decreases t-BHQ-inducible expression of Bcl-xL.(A) Western analysis. Hepa-1 cells were transfected with control or 25, 50, and 75 nM of Nrf2 siRNA. Forty-eight hours after transfection, cells were harvested, lysed, and cell extracts were immunoblotted. (B) Real time-PCR analysis. Hepa-1 cells were transfected with control or Nrf2 siRNA. Twenty-four hours after siRNA transfection, cells were harvested, total RNA extracted and converted to cDNA. The mRNA levels of Bcl-xL and NQO1 were quantified by Real Time-PCR. (C) Real time-PCR analysis. Hepa-1 cells were transfected with control or Nrf2 siRNA (75 nM). Twenty-four hours after siRNA transfection, cells were treated with tBHQ for additional 16h, cells were harvested and total RNA was extracted. The mRNA levels of Bcl-xL and NQO1 were quantified by Real time-PCR. (D) Reporter analysis. Hepa-1 cells were transfected with control or Nrf2 siRNA. Twenty-four hours after transfection, cells were transfected with wild type or mutant Bcl-xL-1.565 (left panels) or with ARE-F1 or mutant ARE-F1 sequences in the pGL2p vector plasmids (right panels), incubated with DMSO or t-BHQ (50µM) for 24h and analyzed for luciferase activity. The data shown are mean ± S.D. of three independent transfection experiments.