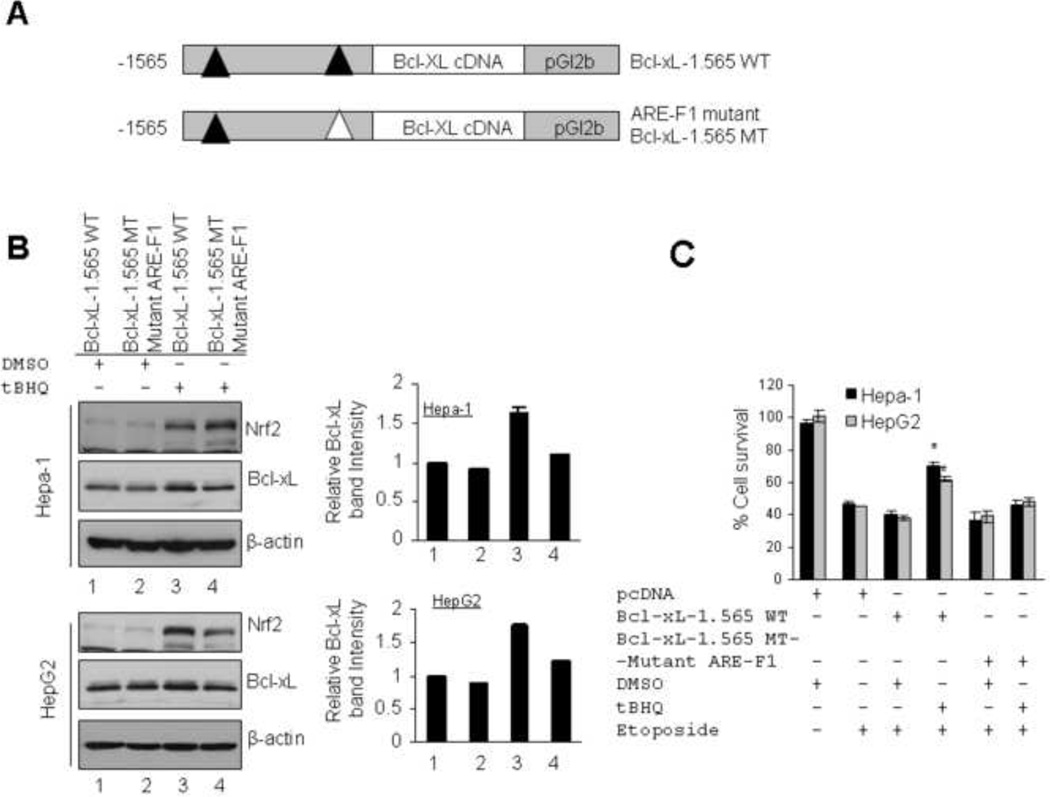
Fig. 8.
Antioxidant (tBHQ) increased Nrf2/Bcl-xL and etoposide-induced cell survival in cells transfected with wild type Bcl-xL-1.565 WT but not in cells transfected with ARE-F1 mutant BclxL-1.565 MT plasmid. (A) Luciferase cDNA was replaced with Bcl-xL cDNA in wild type pGL2b-1.565 WT and ARE-F1 mutant pGL2b-1.565 MT plasmids to generate Bcl-xL-1.565 WT and ARE-F1 mutant Bcl-xL-1.565 MT plasmids. (B) Hepa-1 and HepG2 cells were transfected with wild type pGL2b-1.565 WT and ARE-F1 mutant pGL2b-1.565 MT plasmids, treated with DMSO or tBHQ and immunoblotted (left panels). The Bcl-xL band intensities were quantified and plotted (right panels). (C) MTT assay. Hepa-1 and HepG2 cells were transfected with pcDNA or wild type pGL2b-1.565 WT or AREF1 mutant pGL2b-1.565 MT plasmids. Cells were treated with etoposide alone (Hepa-1; 30 µM, HepG2; 25 µM) or etoposide plus DMSO or tBHQ as indicated and relative cell survival was measured by MTT assay as described in methods section.