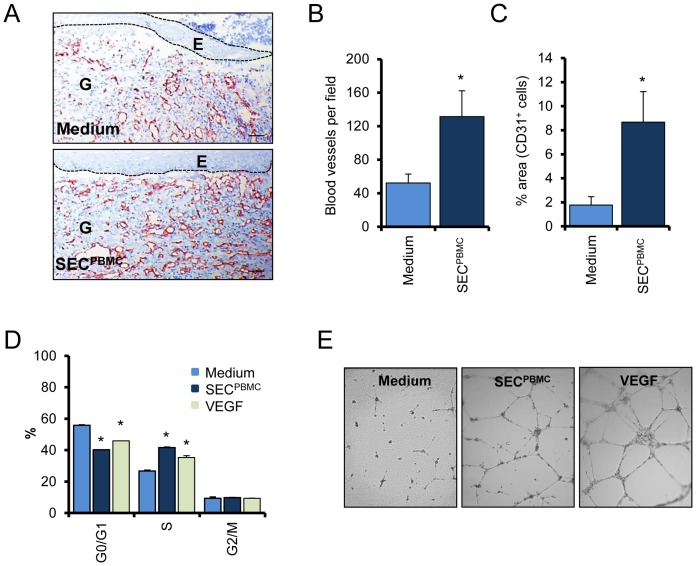
Figure 3. SECPBMC induces formation of new blood vessels.
(A) Representative CD31 stainings of wounds underneath the original wound edge are shown. Scale bars: 50 µm (B) The numbers of CD31 positive cells underneath the newly formed epidermis were evaluated. The graph represents the mean of 15 animals in each group (*: p<0.01). (C) The area of the granulation tissue taken up by CD31+ cells was evaluated. The graph represents the mean of 15 animals in each group. (D) Cell cycle analysis of SECPBMC treated microvascular EC shows a strong increase in proliferating cells. VEGF treatment served as positive control. One representative experiment of three each done in triplicates is shown (*: p<0.01). (E) A tube formation assay is shown. Compared to medium alone SECPBMC strongly induced tube formation in a matrigel assay. One representative experiment of three is shown.