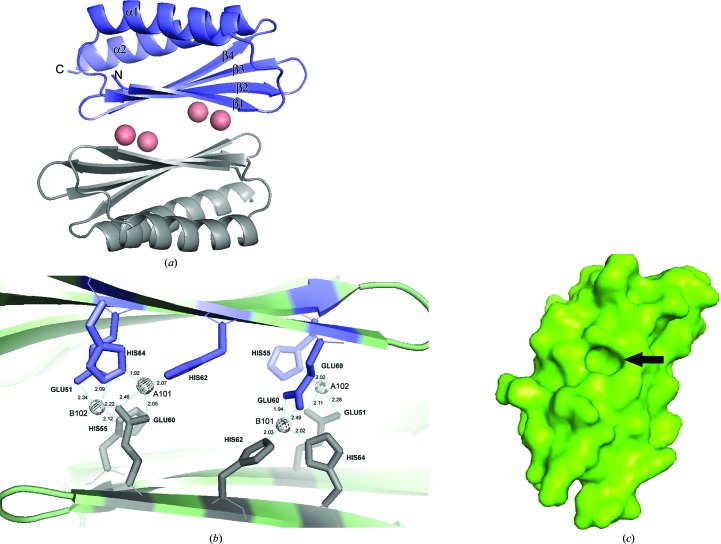
Figure 2.
(a) Cartoon structure of the HPF homodimer. Four cobalts (salmon spheres) coalesce the two monomers and the protein shows an overall β–α–β–β–β–α fold common to several ribosome-associated inhibitor A proteins. α-Helices and β-strands are labeled. (b) shows a close-up of the dimer interface; the spheres are cobalts, which are coordinated by histidines and glutamic acids as indicated. Co atoms are labeled with their PDB designation. (c) A surface representation of a monomer viewed on the dimer interface, with β-strands running from top right to bottom left. The prominent cavity is formed by residues 51-EAT in β3 and the side chains of the flanking residues Gln38 and Ile40 in β2 and His62 and His64 in β4. Slate and gray residues are those from monomers A and B, respectively, in (a) and (b). Figures were generated in PyMOL.