Figure 2.
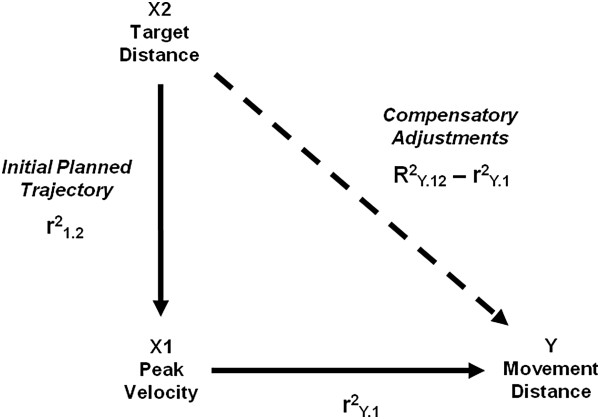
Deterministic statistical model adapted from Gordon & Ghez (1987b). In this model, target distance is hypothesized to influence movement distance (Y) through two pathways. In the initial planned trajectory, target distance influences movement distance through its effect on the initial peak of velocity (X1). The squared correlation coefficient r2Y.1 represents the percentage of variance in final movement distance explained by initial peak velocity. Through a second path, target distance (X2) influences the implementation of corrective adjustments to the trajectory to achieve the distance moved. The additional variance in movement distance accounted for by target distance is equal to the difference between the combined variance accounted for by initial peak velocity and target distance and the variance accounted for by peak velocity alone (R2Y1.2 - r2Y.1).
