Fig. 1. The EGFR signaling pathway is of critical importance to human cancers and of a high complexity.
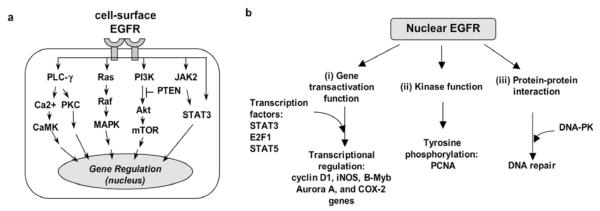
The EGFR signaling pathway exerts its biological effects via two major modes of actions, namely, the cytoplasmic/ traditional (a) and the nuclear (b) signaling modes.
a. The cytoplasmic/traditional EGFR pathway is consisted of five major modules: PLC-γ-CaMK/PKC, Ras-Raf-MAPK, PI-3K-Akt-mTOR, JAK2/STAT3 and STAT3. Activation of these signaling modules often leads to tumorigenesis, tumor proliferation, metastasis, chemoresistance, and radio-resistance.
b. Nuclear EGFR has three key functions: (i) gene transactivation, (ii) tyrosine kinase, and (iii) protein-protein interaction.
