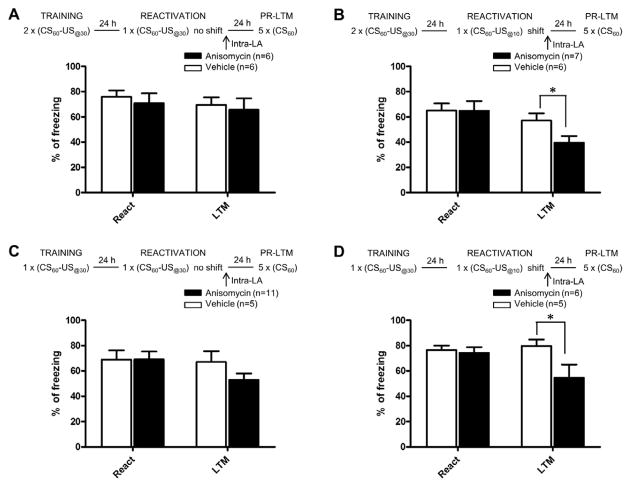
Figure 4. The CS-US time interval is learned at the same time as the CS-US association.
Schematic of the experimental design and percentage of freezing (mean ± s.e.m.) to the CS during reactivation (React) and post-reactivation long-term memory test (PR-LTM) in rats infused in the LA with vehicle (white bars) or anisomycin (black bars). Freezing during reactivation was equivalent between vehicle and anisomycin rats in all experiments. (A, B) Rats trained with 2 CS-US pairings, (A) reactivated with the same CS-US interval than the one learned during training (US@30) and given intra-LA anisomycin did not show an impairment of memory during PR-LTM; in contrast (B), when memory was reactivated with a different CS-US time interval (US@10), anisomycin infused rats showed an impairment of memory. (C, D) The same effect was observed after one-trial training. *P<0.05.