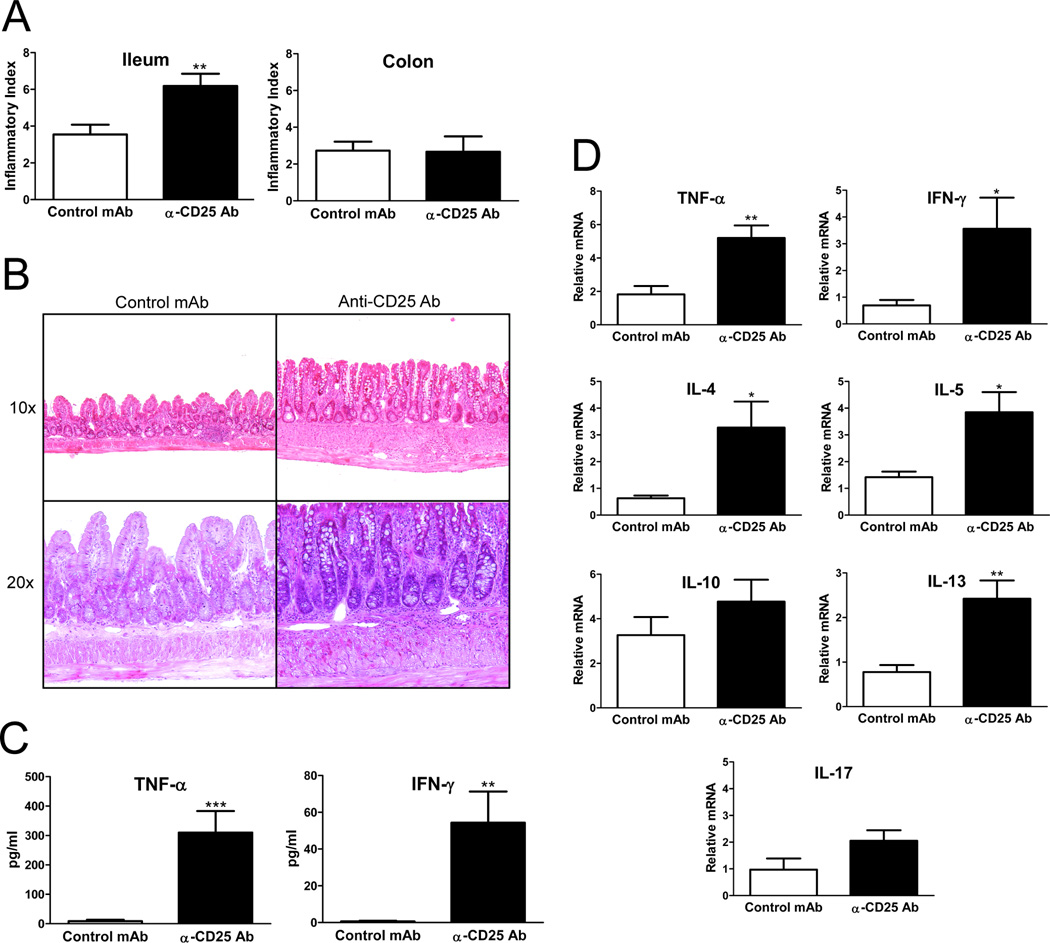
Figure 3. Anti-CD25 Ab treatment increases the severity of spontaneous ileitis in SAMP mice, and increases ileal expression of Th1 and Th2 cytokines.
(A) Anti-CD25 treated mice developed more severe ileitis with a higher mean total inflammatory score compared with control mAb treated mice; no significant colitis was detected in either group (n=11/group). (B) Representative photomicrographs of H&E stained sections, 10× and 20× original magnification. SAMP mice treated with isotype control Ab display minimal inflammatory changes with preservation of the villi morphology; anti-CD25 treated SAMP show increased infiltration of inflammatory cells and villous distortion. (C) Serum TNF-α and IFN-γ levels measured by ELISA were elevated in anti-CD25 treated SAMP mice compared to controls (n=6/group). (D) Total RNA was extracted from ileal tissues from anti-CD25 Ab or isotype control Ab treated SAMP mice, and mRNA was quantified by real-time RT-PCR. Both Th1 and Th2 cytokines were significantly increased in anti-CD25 treated mice. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM (*P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001).