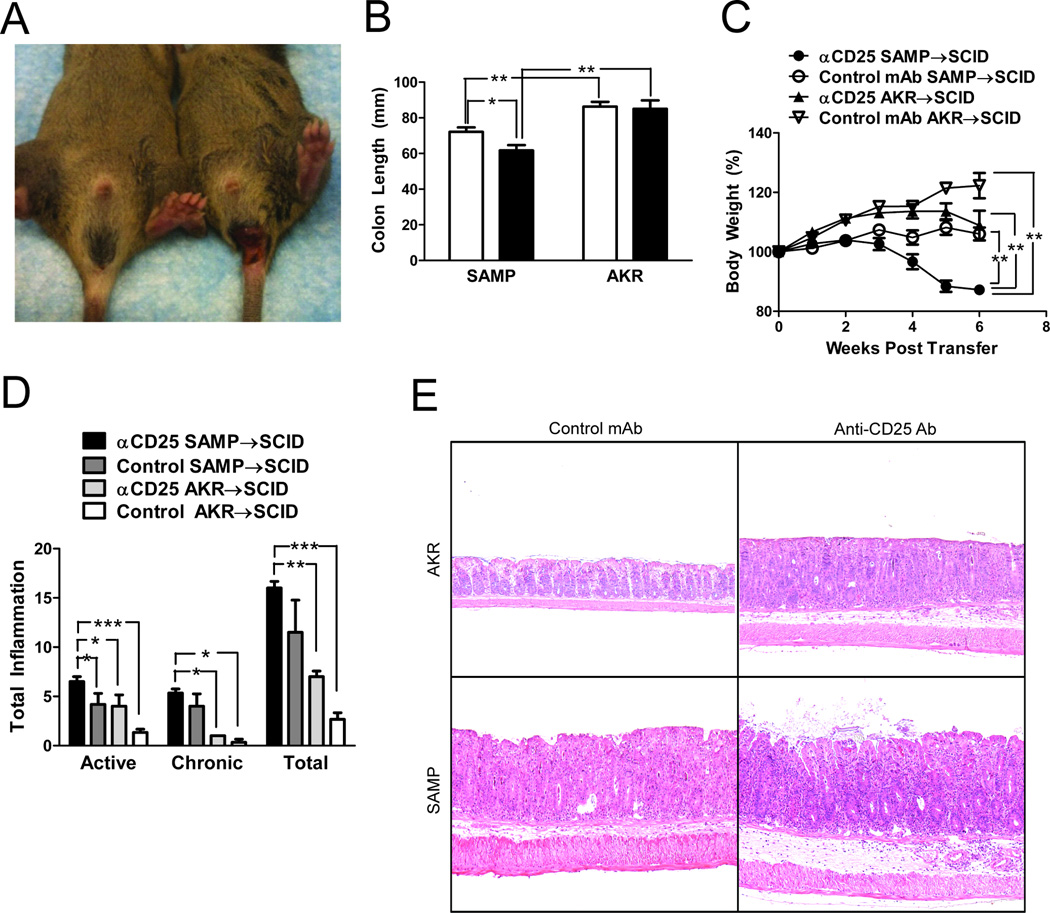
Figure 4. Adoptive transfer of CD4+ cells from anti-CD25 treated SAMP mice induces severe colitis in SCID recipient mice.
2×105 MLN CD4+ cells from anti-CD25 treated or isotype control mAb treated SAMP mice (12wks, n=6/group) were transferred into adult (4–6 wks) MHC-matched SCID mice. Cells were also adoptively transferred into similarly treated AKR control mice (n=4/group). (A) Rectal prolapse occurred in 83.3% of SCID mice that received CD4+ cells for anti-CD25 treated SAMP mice vs. 16.6% that received cells from control mAb treated SAMP mice. (B) Colon length was significantly lower in anti-CD25 treated SAMP mice. (C) Time course of body weight changes after transfer showed significant weight loss in SCID recipients transferred with cells from anti-CD25 treated SAMP compared to the other experimental groups. (D) SCID mice adoptively transferred with CD4+ MLN cells from anti-CD25 treated SAMP mice displayed higher active, chronic, and total inflammatory scores in the colon compared to mice adoptively transferred with cells from treated and untreated AKR donor mice. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM (*P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001). (E) Representative sections from SCID mice adoptively transferred with CD4+ MLN cells from AKR and SAMP mice treated with either anti-CD25 or isotype control Ab. Severe colonic inflammation was observed in SCID mice receiving cells from anti-CD25 Ab SAMP donors.