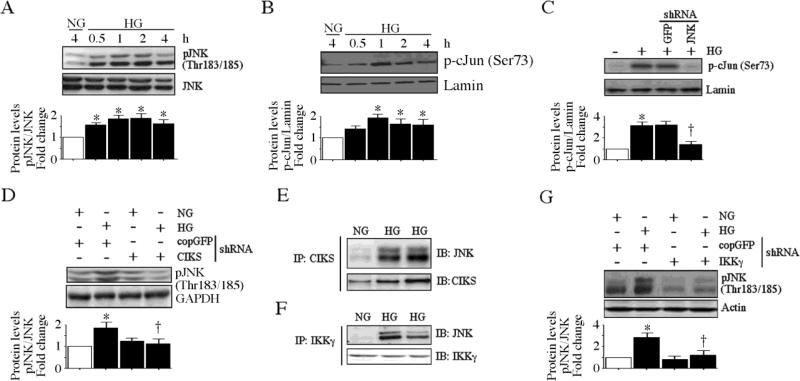
Fig. 7. CIKS mediates high glucose-induced AP-1 activation.
A, HG induces time dependent JNK activation. At 70% confluency, the complete medium on HAEC was replaced with EBM-2 (without supplements) for 2h, incubated with HG for the indicated time periods, and analyzed for phospho-JNK (Thr183/185) levels by immunoblotting (n=3). B, HG induces c-Jun phosphorylation. HAEC treated as in A were analyzed for nuclear phospho-c-Jun (Ser73) levels by immunoblotting (n=3). Lamin B served as a loading and purity control. C, JNK knockdown blunts HG-mediated c-Jun phosphorylation. HAEC infected with lentiviral particles expressing JNK shRNA (MOI 0.5 for 48 h) were treated with HG (1 h) and analyzed for nuclear phospho-c-Jun levels by immunoblotting (n=3). D, CIKS knockdown blunts HG-induced JNK activation. HAEC infected with lentiviral particles expressing CIKS shRNA (MOI 0.5 for 48 h) were treated with HG (1 h) and analyzed for phospho-JNK levels by immunoblotting (n=3). E, HG increases CIKS physical association with JNK. HAEC treated with HG for 15 min were analyzed for CIKS/JNK binding by immunoprecipitation/immunoblot (IP/IB) using whole cell lysates (n=3). F, HG increases JNK physical association with IKKγ. HAEC treated as in E were analyzed for JNK/IKKγ binding by IP/IB using whole cell lysates (n=3). G, IKKγ knockdown blunts HG-induced JNK activation. HAEC infected with lentiviral particles expressing IKKγ shRNA (MOI 0.5 for 48 h) were treated with HG (1 h) and analyzed for phospho-JNK levels by immunoblotting (n=3). A, B, C, D and G, densitometric analysis of three independent experiments is summarized in respective lower panels. *P < at least 0.01 vs. NG, †P < 0.05 vs. HG.