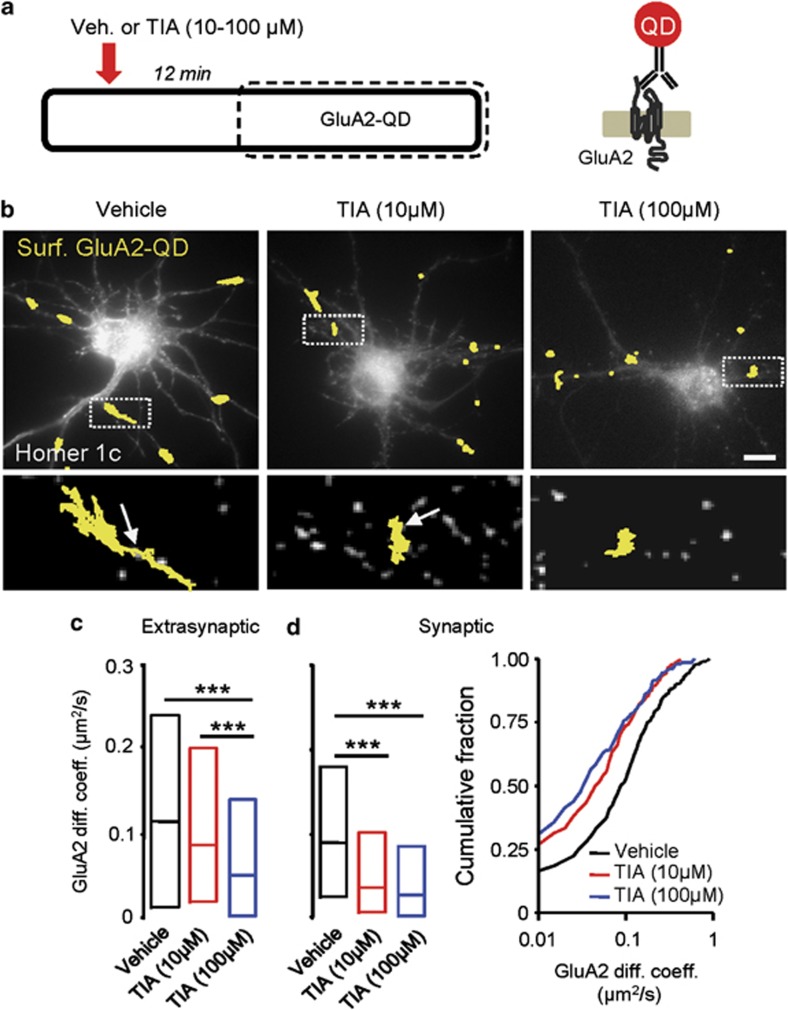
Figure 1.
GluA2-AMPAR surface diffusion is rapidly decreased by tianeptine (TIA) application. (a) Experimental scheme showing that 12 min after the incubation of TIA, surface GluA2-AMPARs were tracked for 20 min in the extrasynaptic and synaptic compartments of days in vitro (DIV) 11–12 cultured hippocampal neurons using quantum dot (QD) coupled to the antibody specific for the extracellular domain of endogenous GluA2 subunit. (b) Typical QD trajectory (yellow) in neurons treated with vehicle (left panel), TIA (10 μM) (middle panel) and TIA (100 μM) (right panel). (Lower panels) Enlarged single GluA2-AMPAR-QD trajectories. The arrows represent homer1c cluster, that is, synapses. Scale bar=10 μm. (c) Diffusion coefficients (median±25–75% interquartile range (IQR)) of extrasynaptic GluA2-AMPARs was decreased in neurons incubated with TIA (10 and 100 μM) compared to vehicle-treated neurons (vehicle=0.11±0.022–0.24 μm2 s−1, n=753; TIA (10 μM)=0.087±0.025–0.20 μm2 s−1, n=446; TIA (100 μM)=0.055±0.007–0.142 μm2 s−1, n=255; ***P<0.001). (d) Synaptic GluA2-AMPAR diffusion coefficient was also decreased after TIA incubation (10 and 100 μM) (vehicle=0.08±0.03–0.18 μm2 s−1, n=281; TIA (10 μM)=0.04±0.01–0.11 μm2 s−1, n=245; TIA (100 μM)=0.03±0.007–0.09 μm2 s−1, n=214; ***P<0.001). (Right panel) Cumulative distributions of diffusion coefficients of neurons treated with vehicle or TIA (10 and 100 μM). Note the shift toward the left in the presence of TIA, indicating a reduced GluA2-AMPAR surface diffusion immobilized at synapses.