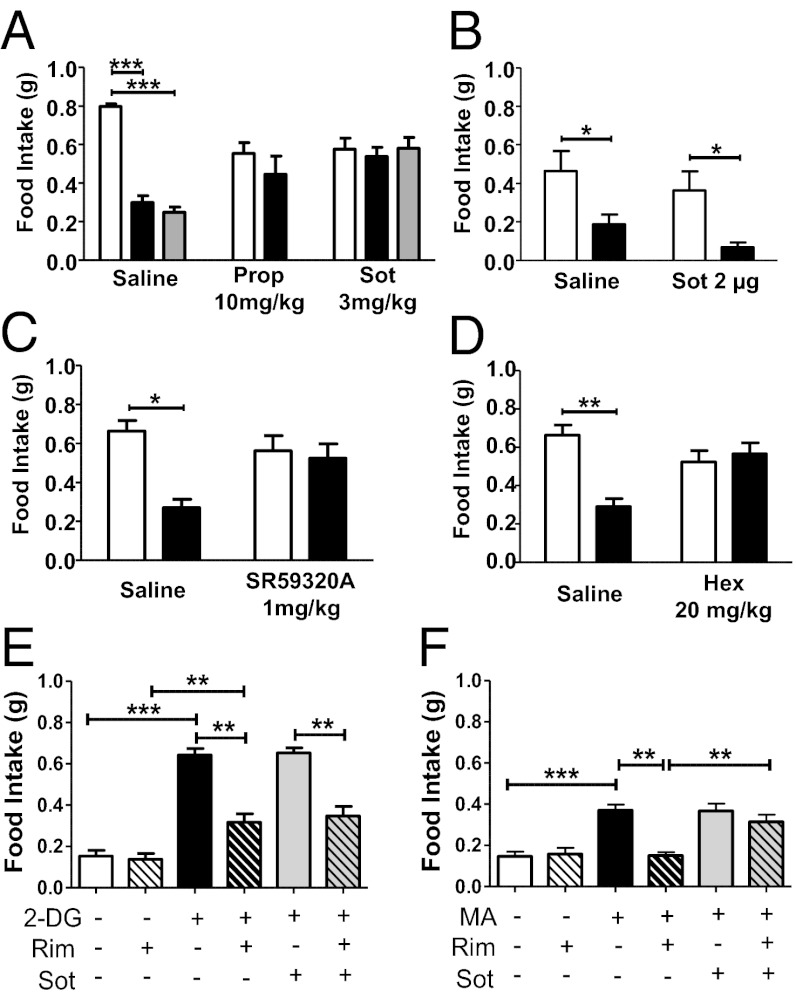
Fig. 2.
Blockade of peripheral β-adrenergic receptors prevents rimonabant-induced hypophagia. Effect of rimonabant (black bars, 3 mg/kg, i.p.; gray bars, 10 mg/kg, i.p.) or its vehicle (white bars) in fasted mice pretreated with (A) the β-blocker propranolol (Prop, 10 mg/kg, i.p.) or with the peripherally restricted β-blocker sotalol (Sot, 3 mg/kg, i.p.); (B) the β-blocker sotalol administered centrally (2 μg intracerebroventricularly); (C) the selective β3-blocker SR59320A (1 mg/kg, i.p.); (D) the ganglionic blocker hexamethonium (Hex, 20 mg/kg, i.p.). (E) Effect of β-blocker sotalol (3 mg/kg, i.p.) and rimonabant (Rim, 3 mg/kg, i.p.) in conditions of glucoprivation induced by 2-DG injection (250 mg/kg, i.p.). (F) Effect of β-blocker sotalol (3 mg/kg, i.p.) and rimonabant (3 mg/kg, i.p.) in conditions of lipoprivation induced by MA injection (68 mg/kg, i.p.). Data are means ± SEM. n = 5–8 mice per group. Statistics by two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s posttest. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.