Fig. 3.
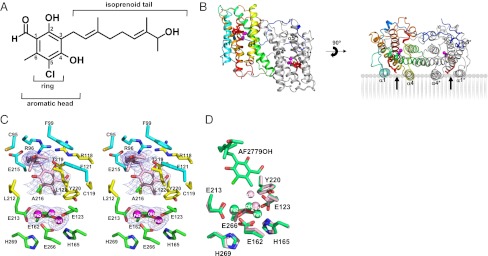
Structure of the TAO–AF2779OH complex. (A) The chemical structure of AF2779OH. (B) Overall structure of the TAO–AF2779OH complex. AF2779OH is shown as a red stick. Chains A and B are shown as rainbow (colored blue to red from N to C terminus) and gray, respectively. The AF2779OH-binding cavity is shown by an arrow. (C) Stereo view of the AF2779OH binding region of chain A. The residues that interact with AF2779OH (pink stick) -ring and -tail are shown as yellow and cyan sticks, respectively. N, O, and Cl atoms are colored in blue, red, and green, respectively. Sigma-A weighted electron density map calculated from the refined model of the TAO–AF2779OH complex with the diiron centers and AF2779OH molecules omitted from the phase calculation is also shown. Contour levels are 1.0 σ (blue) and 3.0 σ (orange). (D) Superimposed diiron active sites of AF2779OH-free (light pink) and -bound (green) forms of TAO. The binding of AF2779OH causes the formation of a coordinate bond between H165 and Fe1.
