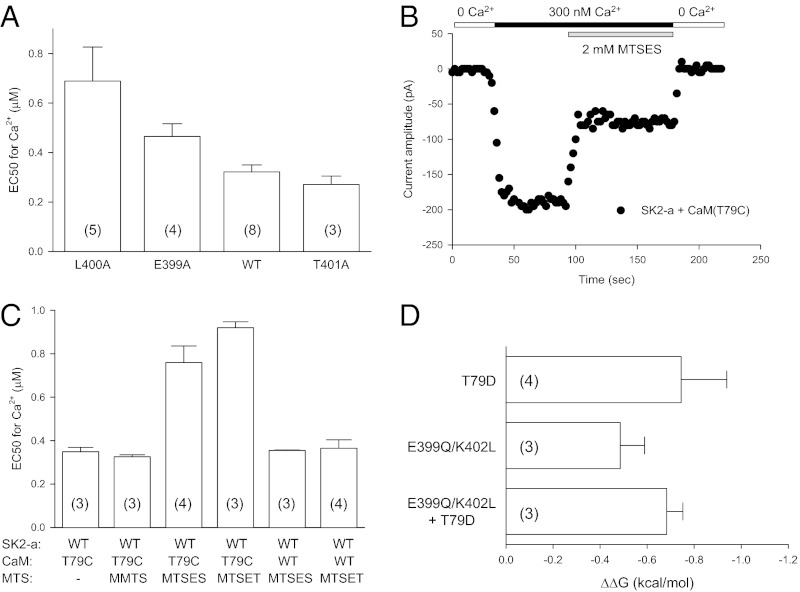
Fig. 2.
Effects of the cuff–CaM linker interaction on SK channel activation. (A) L400A and E399A mutants become less responsive to Ca2+ for their activation, but T401A does not produce significant changes in its Ca2+-dependent activation. Values in parentheses indicate the number of experiments. (B) Application of MTSES to T79C reduces the SK channel current amplitude. (C) Effects of T79C (CaM) and application of MTS reagents on Ca2+-dependent channel activation. MMTS, MTSES, or MTSET was mixed in the bath solution with 300 nM Ca2+ just before their application during recording. (D) Changes in Gibbs free energy (ΔΔG) for the CaM:SK2-a pairs T79D:WT, WT:E399Q/K402L, and T79D:E399Q/K402L. No statistical differences were found for ΔΔG among the three pairs, suggesting the direct interaction between the CaM linker and the channel cuff.