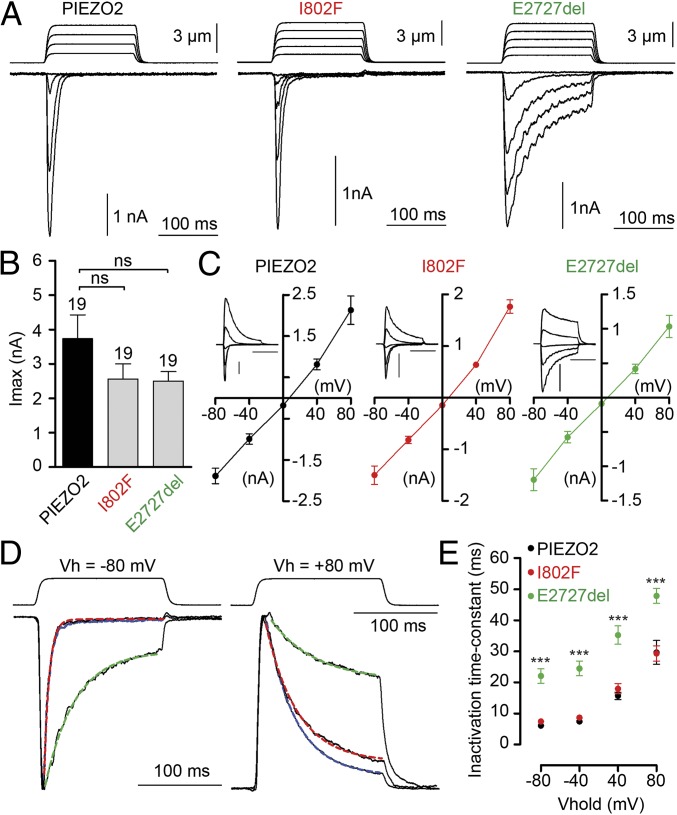
Fig. 2.
E2727del PIEZO2 channels display slower inactivation kinetics compared with wild type. (A) Representative traces of MA inward currents at –80 mV in cells transfected with the indicated constructs and subjected to a series of mechanical steps in 1 µm increments. (B) Average maximal current amplitude of MA inward currents at –80 mV. The number of cells tested is shown above bars. (C) Averaged current-voltage relationships of MA currents in cells transfected with hPiezo2 (n = 7 cells), I802F (n = 8 cells), or E2727del (n = 8 cells). The insets show representative MA currents evoked at holding potentials ranging from –80 to +80 mV; inset scale bars are 1 nA and 100 ms. (D) Representative traces of MA currents elicited at –80 and +80 mV holding potentials. Traces were normalized to the peak current, and blue, red, and green dashed lines represent fits of inactivation with a monoexponential equation of human PIEZO2, I802F, and E2727del currents, respectively. (E) Time-constant of inactivation (tau) of PIEZO2 (black dots, n = 7 cells), I802F (red dots, n = 8 cells), and E2727del (green dots, n = 8 cells) currents at different holding potentials. Dots and bars represent mean ± SEM. ns, not statistically different; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; Mann–Whitney test.