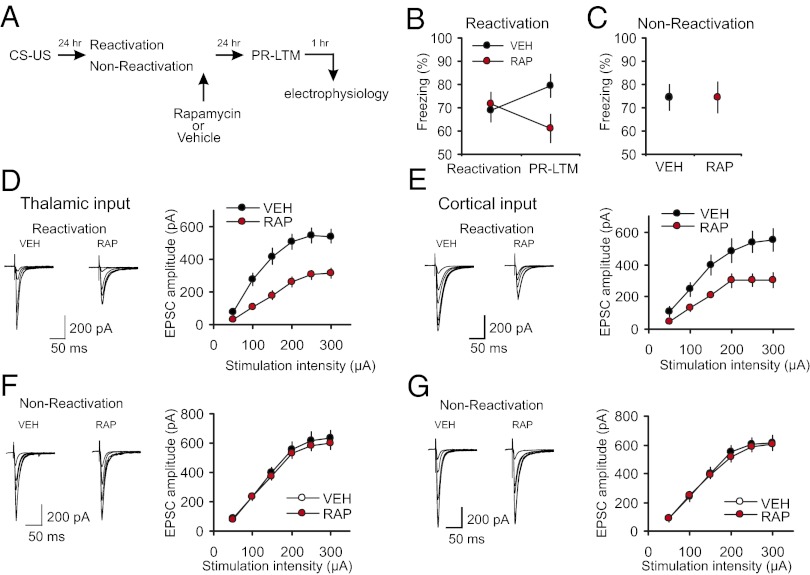
Fig. 2.
Postretrieval rapamycin impairs reconsolidation of fear memory and suppresses conditioning-induced synaptic enhancements. (A) A schematic representation of the experiments where fear-conditioned rats received a postretrieval injection of rapamycin (RAP; 20 mg/kg, i.p.) or vehicle (VEH). (B) There was no significant difference in percent freezing between VEH-treated (n = 29) and RAP-treated (n = 29) rats during memory reactivation (t test, P = 0.74). The difference in freezing between reactivation and PR-LTM tests in the VEH group did not reach the level of statistical significance (P = 0.06). A significant impairment was observed in RAP rats during the PR-LTM test (see text for details). (C) Rapamycin had no effect on conditioned freezing in “nonreactivated” control rats. Rats in nonreactivation group received rapamycin or vehicle injections at 24 h postconditioning without memory reactivation and PR-LTM was tested 24 h after the injections (RAP, n = 16 rats; VEH, n = 8 rats; t test, P = 0.9 for VEH group vs. RAP group). (D, Left) Averaged EPSCs evoked in thalamic input to the LA by stimuli of increasing intensity in slices from fear-conditioned rats which received postreactivation injections of VEH or RAP. (D, Right) Synaptic input–output curves obtained in thalamic input in slices from both groups of rats (VEH, n = 12 neurons; RAP, n = 13 neurons (two-way ANOVA, P < 0.001 for VEH group versus RAP group of conditioned rats). (E) Experiments were analogous to D, but the EPSCs were recorded in cortical input to the LA (VEH, n = 12 neurons; RAP, n = 8 neurons; two-way ANOVA, P < 0.001). (F) Rapamycin or vehicle were injected at 24 h postconditioning without memory reactivation and synaptic input–output curves were obtained in thalamic input 24 h after the injections (VEH, n = 14 neurons; RAP, n = 23 neurons; two-way ANOVA, P = 0.275). (G) Experiments were analogous to F but the EPSCs were recorded in cortical input (VEH, n = 9 neurons; RAP, n = 19 neurons; two-way ANOVA, P = 0.515). Results are shown as means ± SEM.