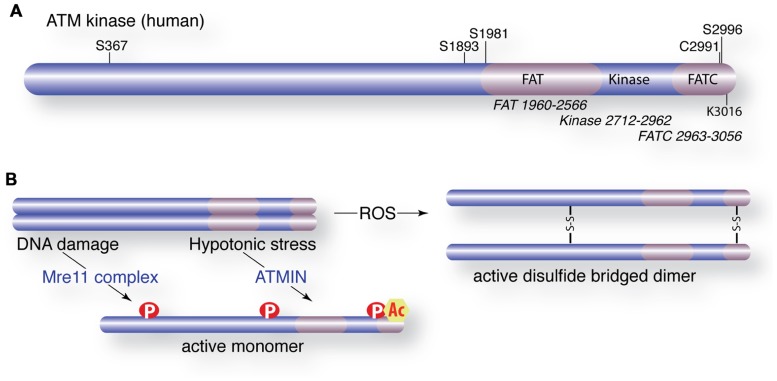
FIGURE 2.
Activation of ATM and post-translational modifications. (A) Schematic of the ATM protein with domain organization (FAT = FRAP, ATM, and TRAP). Major autophosphorylation sites (S367, S1893, S1981, S2996), the TIP60 acetylation site (K3016) and a critical cysteine involved in ROS activation are shown. (B) Activation of ATM by DNA damage or hypotonic stress requires the Mre11 complex (Mre11, Rad50, Nbs1) or ATMIN, respectively. Activated ATM is monomeric, phosphorylated and acetylated. Alternatively, ATM is activated directly by ROS that oxidizes cysteine residues to promote disulfide bridge-mediated dimerization.