Figure 1.
Trichostatin A Blocks the Emergence and Maintenance of Drug Resistance in C. albicans and S. cerevisiae
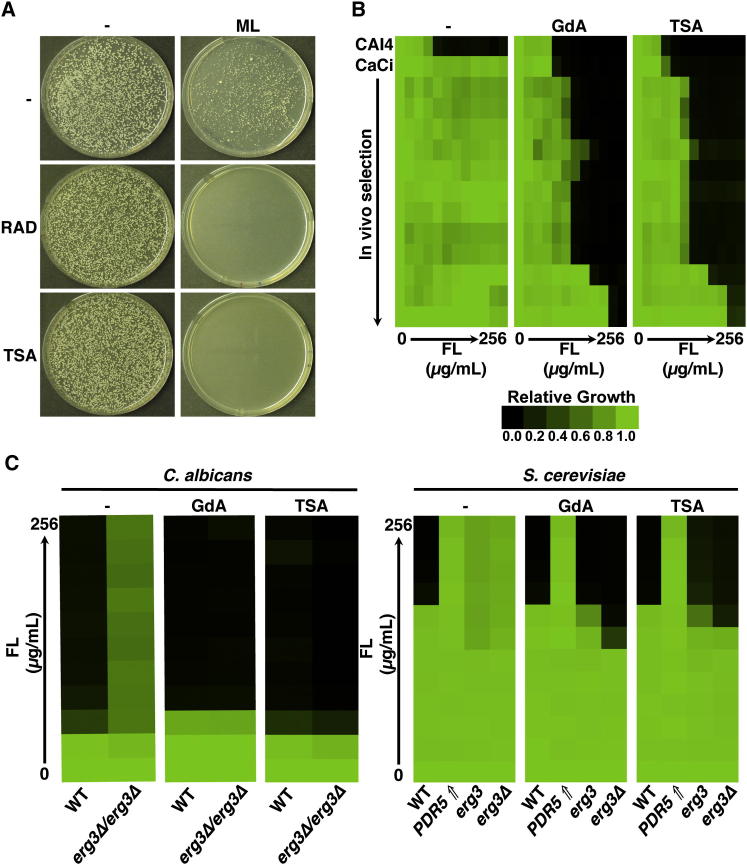
(A) A total of 1 × 105 cells of a wild-type C. albicans strain was plated onto YPD with no drug (−), 800 nM of the azole miconazole (ML), 1 μM of the Hsp90 inhibitor radicicol (RAD), 6 μg/ml of the KDAC inhibitor trichostatin A (TSA), or a combination of azole and inhibitor, as indicated.
(B) Fluconazole (FL) resistance of C. albicans clinical isolates is abrogated when KDACs are inhibited. MIC assays were conducted in YPD with no inhibitor (−), with the Hsp90 inhibitor geldanamycin (GdA, 5 μM), or with TSA (6 μg/ml). C. albicans clinical isolates (CaCis) are ordered sequentially with those recovered early in treatment at the top. Data are quantitatively displayed with color using TreeView (see bar).
(C) TSA specifically reduces FL resistance of C. albicans and S. cerevisiae Hsp90-dependent azole-resistant mutants. MIC assays were conducted in YPD with no inhibitor (−), with GdA (1 μM for C. albicans, 5 μM for S. cerevisiae), or with TSA (6 μg/ml). Growth and analysis are as in (B). PDR5⇑ represents a S. cerevisiae strain that acquired FL resistance by upregulation of the drug efflux pump Pdr5. erg3 represents a S. cerevisiae strain that acquired FL resistance due to a loss-of-function mutation in ERG3.
See also Table S1.