Figure S5.
RUNX1 ChIPseq and AF4-MLL Complex Data, Related to Figure 6
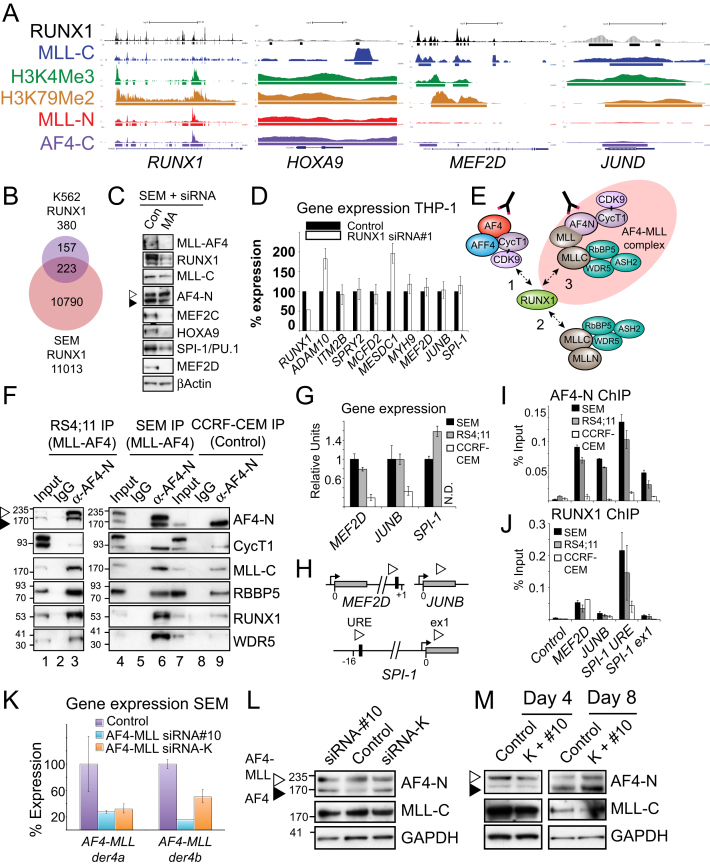
(A) Sample ChIP-seq tracks from SEM cells across RUNX1, HOXA9, MEF2D and JUND.
(B) ChIP-seq overlap between the RUNX1 SEM cell target gene set versus the set of RUNX1 target genes from (Pencovich et al., 2011).
(C) Western blots for the proteins indicated in SEM cells treated with a scrambled control or an MLL-AF4 siRNA. Proteins were detected using the antibodies indicated except MLL-AF4, which was detected with an AF4-C antibody.
(D) Gene expression analysis of selected genes in THP-1 cells treated with RUNX1 siRNA (siRNA#1). For each experiment, the PCR signal was quantified relative to the appropriate control treated cells. Results represent the average of three independent knockdown experiments, and error bars represent the standard deviation between experiments.
(E) A schematic of protein complex interactions centering on the RUNX1 protein. RUNX1 can interact with a wild-type AF4 complex (interaction 1) through CyclinT1 (Elagib et al., 2008; Jiang et al., 2005), a wild-type MLL-C complex (interaction 2) and potentially with an AF4-MLL complex (interaction 3).
(F) Immunoprecipitation (IP) experiments using RS4;11 (t(4;11)), SEM (t(4;11)) and CCRF-CEM (wild-type MLL1) nuclear extracts. Extracts were IP’d with either αAF4-N (lane 3, 6 and 9) or a control αIgG (lane 2, 5 and 8) antibody, blotted and probed with the antibodies indicated. Lane 1,4 and 7 (Inputs) represents 1% of the amount of extract used for the IPs. AF4-MLL is indicated by a white arrowhead (AF4-MLL is 328 KDa, the white arrowhead represents the ∼194KDa Taspase 1 cleaved product) while wild-type AF4 is indicated by a black arrowhead (wild-type AF4 has a predicted size of 131 KDa but an apparent MW of 175 KDa). MLL-C is the Taspase 1 cleaved product of both AF4-MLL and wild-type MLL which is 134KDa but runs with an apparent MW of 180KDa.
(G) Real Time PCR of MEF2D, JUNB and SPI-1 expression in SEM, RS4;11 and CCRF-CEM cells.
(H) A schematic of the MEF2D, JUNB and SPI-1 (aka PU.1) loci showing the approximate location of PCR primer sets (open arrow heads) used for ChIP analysis. Black box = consensus RUNX1 binding motifs in the upstream regulatory region (URE) of SPI-1 (Huang et al., 2008; Huang et al., 2011). and the first intron of MEF2D (Pencovich et al., 2011). Grey box = exon1 of MEF2D, JUNB and SPI-1.
(I and J) ChIP analysis in SEM (black bars), RS4;11 (gray bars), CCRF-CEM (white bars) at the targets as indicated using antibodies to AF4-N (I) or RUNX1 (J).
(K) Real Time PCR expression of AF4-MLLder4a and der4b (Kumar et al., 2011) in SEM cells treated with a scrambled control (purple bars), an AF4-MLL siRNA (siRNA#10, blue bars) or an AF4-MLL siRNA (siRNA-K, orange bars) from (Kumar et al., 2011). Error bars represent the ± SD of three separate PCR reactions. In each individual experiment, control values were arbitrarily set to 100. AF4-MLL siRNA sequences are in supplemental methods.
(L) Western blots of the AF4-MLL knockdowns in (K) using the antibodies indicated. The apparent MW of AF4-MLL and MLL-C is explained in (F) above.
(M) Western blots at day 4 and day 8 of SEM cells treated with both AF4-MLL siRNA-K and siRNA#10 at day 0, day 2, day 4 and day 7. Antibodies are as indicated. AF4-MLL is indicated by a white arrowhead while wild-type AF4 is indicated by a black arrowhead as explained in (F) above.