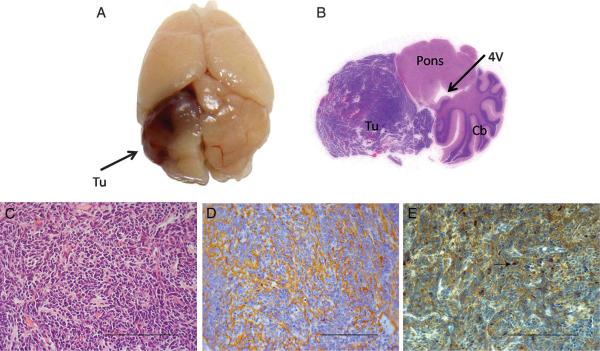
FIGURE 3.
RCAS wild-type p53-induced phosphatase 1 (WIP1) cooperates with RCAS sonic hedgehog (SHH) to induce MB in the cerebellum of Ntv-a mice. A, gross specimen of brain of Ntv-a mouse 3 months after co-injection of RCAS-WIP1 and RCAS-SHH demonstrating tumor (Tu) in the cerebellar hemisphere. B, whole-mount hematoxylin and eosin of Ntv-a mouse cerebellum (Cb) after injection of RCAS-WIP1 and RCAS-SHH demonstrating tumor formation with mass effect on the fourth ventricle (4V) and brainstem (Pons). C, photomicrograph (×400) of tumor induced by RCAS-WIP1 and RCAS-SHH demonstrating histological features consistent with MB including sheets of monomorphous small cells (Scale bar = 100 μm). D, photomicrograph (×400) of tumor induced by RCAS-WIP1 and RCAS-SHH demonstrating positive staining for synaptophysin, a marker of neuronal tumors (scale bar = 100 μm). E, photomicrograph (×400) of tumor induced by RCAS-WIP1 and RCAS-SHH. Arrow indicates positive staining for WIP1 in the nucleus of a tumor cell. (Scale bar = 100 μm).