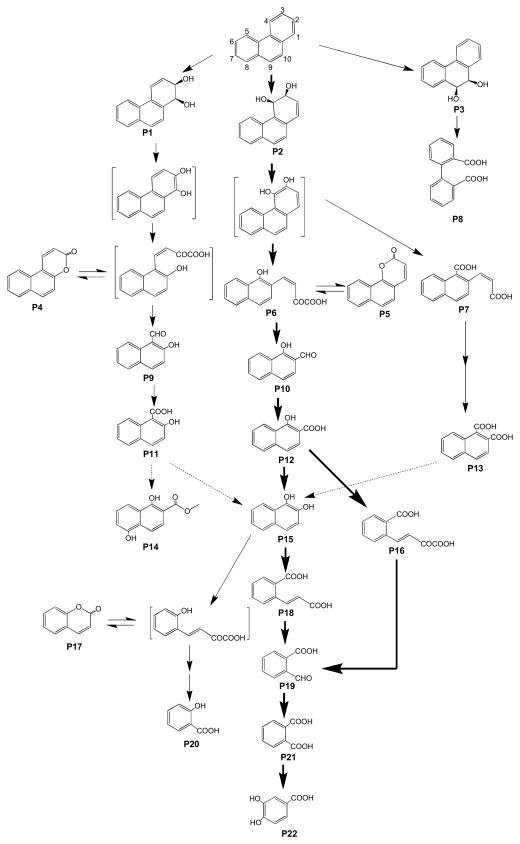
Fig. 3.
Proposed metabolic pathways of phenanthrene by S. maltophilia strain C6. Carbon atoms in phenanthrene was numbered. The compounds are 1,2-dihydroxyphenanthrene (P1), 3,4-dihydroxyphenanthrene (P2), cis-9,10-hidroxyphenanthrene (P3), 5,6-benzocoumarin (P4), 7,8-benzocoumarin (P5), methyl trans-4-(1-methoxy-2-naphthyl)-2-oxobut-3-enoate (P6), 2-carboxyvinyl-1-naphthoate (P7), 2-2′-diphenic acid (P8), 2-hydroxy-1-naphthaldehyde (P9); 1-hydroxy-2-naphthaldehyde (P10); 2-hydroxy-1-naphthoic acid (P11); 1-hydroxy-2-naphthoic acid (P12); naphthalene-1,2-dicarboxylic acid (P13), 1,4-dihydroxy-2-naphthoic acid methyl ester (P14), naphthalene-1,2-diol (P15), 2-carboxybenzalpyruvate (P16), coumarin (P17), 2-carboxycinnamic acid (P18), 2-formylbenzoic acid (P19), salicylic acid (P20), phthalic acid (P21), and protocatechuic acid (P22). Bold and thin arrows: major and minor pathways, respectively; dotted line arrow, tentative pathway. Metabolites in brackets, not detected.