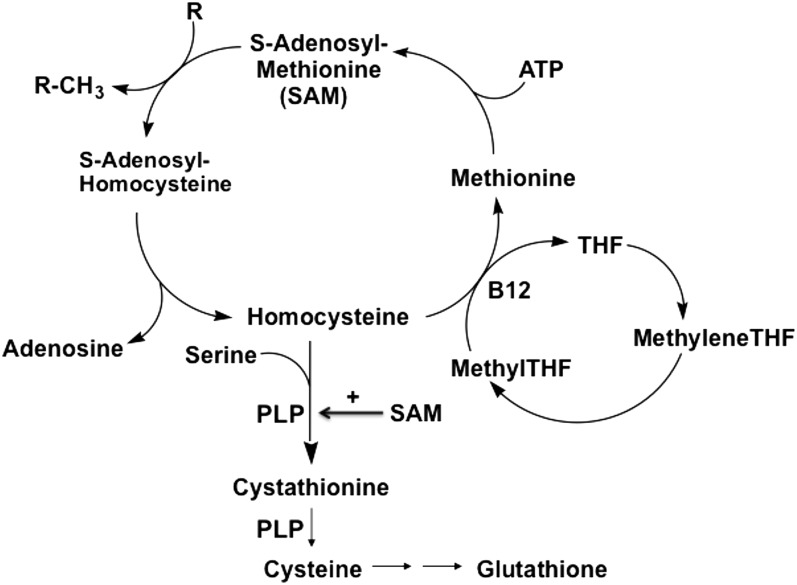
FIGURE 1.
Homocysteine metabolism. Folate, in the form of methylTHF, and vitamin B-12 serve as substrate and cofactor, respectively, in the remethylation of homocysteine to form methionine and SAM. SAM serves as an allosteric activator of cystathionine β-synthase, the enzyme that converts homocysteine to cystathionine. Vitamin B-6, in the form of PLP, serves as a cofactor in the conversion of homocysteine to cystathionine and then to cysteine. Deficiencies of folate, vitamin B-12, and vitamin B-6 cause increased homocysteine and decreased cysteine (27). B12, vitamin B-12; methyleneTHF, methylenetetrahydrofolate; methylTHF, methyltetrahydrofolate; PLP, pyridoxal-5′-phosphate; R, methyl acceptor; R-CH3, methylated acceptor; SAM, S-adenosylmethionine; THF, tetrahydrofolate.