Figure 1. Quasi-processive phosphorylation model under the condition of macromolecular crowding.
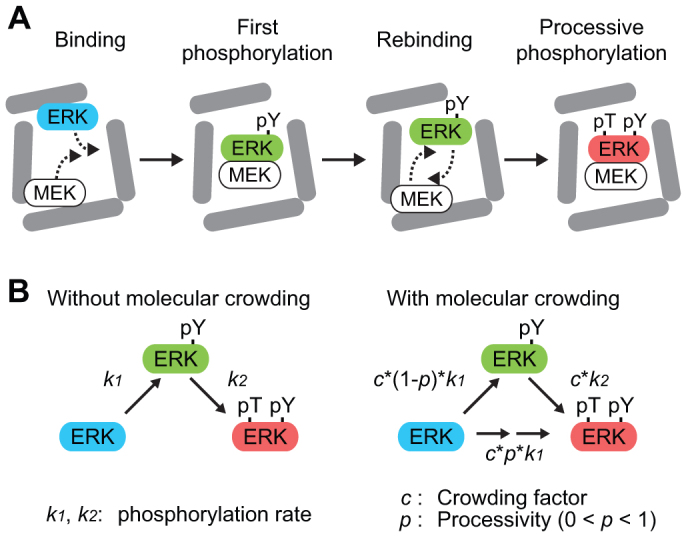
(A) MEK (white) binds to and phosphorylates np-ERK (blue) at the tyrosine residue in the activation loop, and then dissociates from the product, pY-ERK (green). Under the condition of macromolecular crowding, the diffusions of both MEK and pY-ERK are restricted by the cage effect of the crowder molecules (grey). Thus, MEK rebinds to and phosphorylates pY-ERK with high probability. Consequently, MEK phosphorylates ERK in a processive manner, and produces pTpY-ERK (red). (B) The distributive (left) and quasi-processive phosphorylation model (right) are represented with parameters, including the phosphorylation rate constants, k1 and k2, crowding factor, c, and processivity, p.
