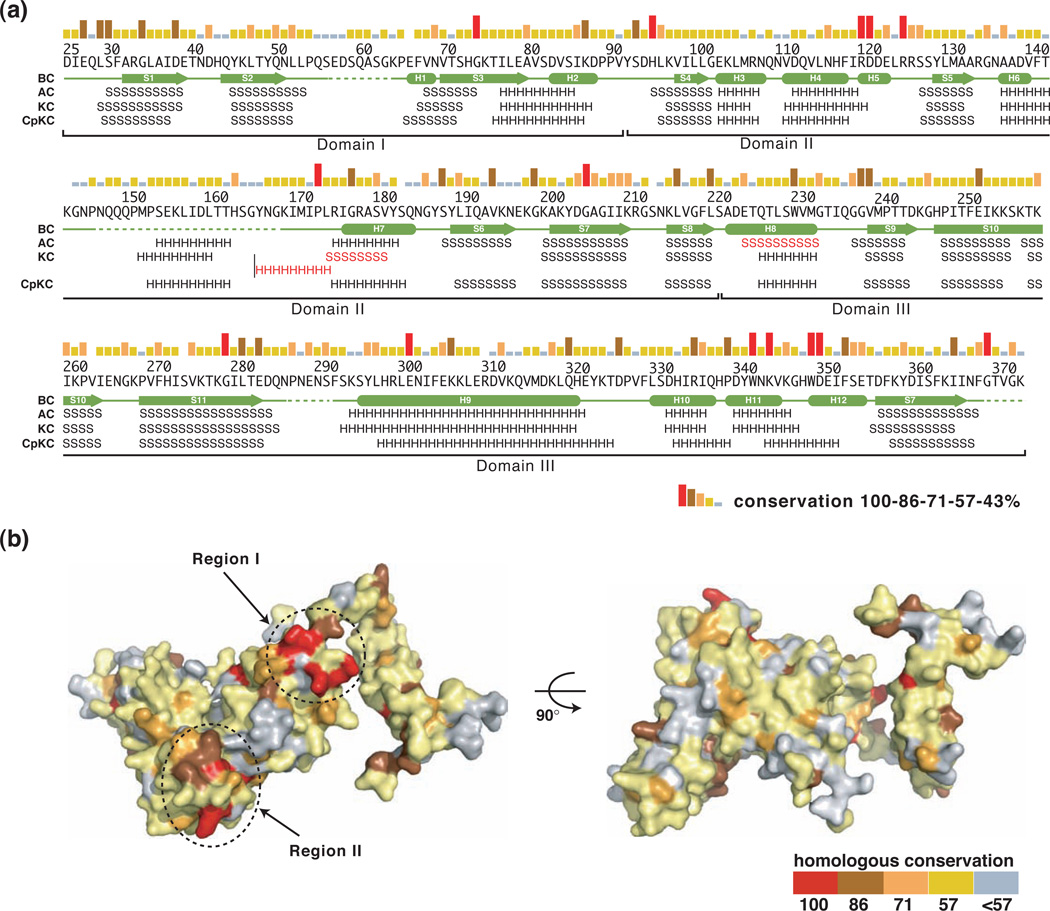
Figure 2. a,b. Sequence conservation between GerBC and its homologs.
(a) Sequence conservation and secondary structure elements for GerBC and its homologs. Sequence conservation is shown as a bar graph, with red bars indicating identity among the seven GerBC homologs from B. subtilis and the closely related species B. amyloliquefaciens, B. pumilus, B. clausii, and B. cereus (see also Figure S6). Secondary structure assignments of GerBC (BC) from the crystal structure are shown as green cylinders (α helices) and arrows (β strands), while disordered regions are shown as dashed lines. Predicted secondary structure elements (http://www.predictprotein.org) for B. subtilis GerAC and GerKC (AC and KC, respectively), and C. perfringens GerKC (CpKC) are indicated by letters (“H”: α helix; “S”: β strand) and the major differences are highlighted in red.
(b) Molecular surface of GerBC colored according to homologous conservation.