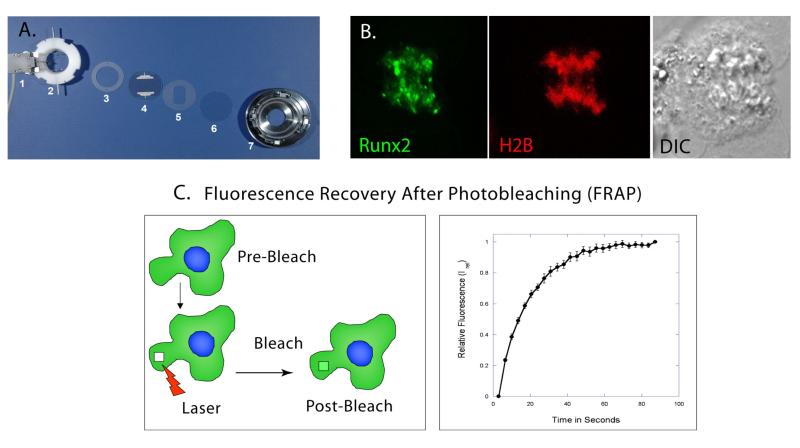
Figure 3. Live Cell Microscopy by Confocal Laser Scanning.
A. The Bioptics Live Cell Stage-Closed System Chamber allows the viewing of living cells by maintaining 37°C temperature; pH and nutrient supply by perfusing media across a cell-laden coverslip. The slide heater (1) warms an Aqueduct Slide (4) to 37°C. The Perfusion Ring Chamber (2) allows media to enter, cross and exit the chamber, and Gaskets (3, 5) sandwich the Aqueduct Slide and cell-laden coverslip (6) to prevent leaks. This assembly sits in the self-locking base (7) that is placed on the microscope stage. B. Live image of U2-OS cell in Anaphase. Runx2-EGFP foci (green) localize to mitotic chromosomes in Anaphase. Histone 2B-RFP and Differential Interference Contrast (DIC) images are used to identify mitotic stage. C. Initially, using high intensity laser power, a Spot or Region of Interest inside the fluorescent cell is bleached. After bleaching, a series of images are taken at predetermined time intervals to measure the recovery of fluorescence in the bleached spot (Left Panel). Y-axis represents the relative fluorescence after photo bleaching in the bleached spot and X-axis represents time in seconds. Post normalization, the relative fluorescence in the bleached spot is zero. This time point is represented as zero time. The relative fluorescence increases with time until it reaches asymptote (Right Panel).